When you need a custom injection mold for your injection molding project, the first choice you may have to make is whether to choose an aluminum injection mold or a steel injection mold. Molds made of different materials will affect the quality, accuracy, molding cycle, cost and delivery time of plastic parts. In this guide, we specially ask experts in the field of molds to tell you the differences between aluminum molds and steel molds, and how you should choose.
Read on to learn more about the two most popular types of injection molds.
Table of Contents |
Turnaround Time

Turnaround time is the time between the start of mold development and the time the part is ready for production. The design methods and calculations for the two types of molds are actually different, but the manufacturing stage is where significant changes occur.
Aluminum injection molds are made from aluminum blanks using CNC machining and finishing operations. In some cases, additional electrical discharge machining (EDM) is required if the cavity must have sharp corners that cannot be obtained by milling.
Usually, processing is mainly mechanical processing, no heat treatment is required, and almost no specialized tools are required. The average aluminum cavity is produced in 10 to 15 days.
Steel molds are made in a similar way, but there are some differences. First, the material is much harder and takes longer on the machine, wearing out the cutting tools and requiring specialized tools. Second, extensive heat treatment operations are required to increase mold life. All of this takes time.
Typically, steel molds take 2 to 5 months to complete.
Stability Comparison

Stability is basically the number of parts a mold can produce before it becomes too old. Important parameters to consider if you want to produce a batch of product.
Steel molds are specifically designed to last. They have minimal seams and are made from the most durable steel. That's why they can withstand millions of parts.
Aluminum molds are made from softer materials, however, some aluminum alloys offer exceptional strength. This allows the mold to withstand up to 5,000 parts. Average is 100-2000 copies
Part Manufacturing Time Comparison
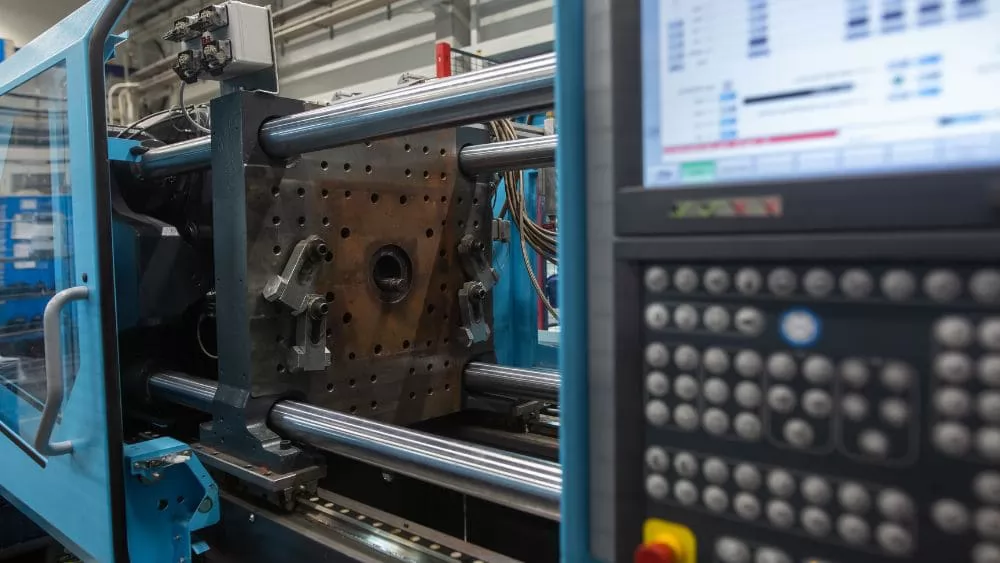
When a product must be produced in batches, the manufacturing time of each part becomes an important factor. Manufacturing time is the time between injecting the liquid polymer and ejecting the final part. This factor varies with mold material, injection pressure and temperature.
Steel molds can withstand the highest injection pressures and temperatures, which is why the manufacturing process may only take 5 to 10 seconds.
Aluminum molds are not as strong, so their pressure and temperature are 20-30% lower than steel molds. Manufacturing time is 44-70 seconds, which is quite impressive when we start talking about thousands of parts.
Part Accuracy and Surface Finish Comparison

Part quality is one of the most important factors. After all, this part will serve as an integral part of a larger mechanism and may be presented to future investors. The part must look professional
The accuracy of steel and aluminum injection molds is similar and only depends on the ability to machine and polish it. Modern technology can produce steel and aluminum mold cavities with tolerances up to IT6.
Flexibility Comparison

Flexibility is crucial with pre-production prototypes when you're only testing how the final product will look and operate. Once you have completed initial prototyping using certain materials, you will need to test the materials you initially selected for your product, as well as test your manufacturing procedures. Most of the time, you will encounter some problems that will make you modify the design.
For example, during running tests, some defects were discovered or the injection process resulted in porous parts. That's when you want to change the design as well as the mold. Different mold materials have different flexibility.
Steel molds are hardened by heat treatment. This is usually done after all the basic parts have been machined and only a small layer of material needs to be ground. If certain features need to be modified, it can be difficult because the cavity is very hard.
Aluminum molds are made from softer materials, and their cavities are typically manufactured as separate parts that fit into the mold base. Therefore, it is much easier to remove the cavity and make adjustments.
Mold Cost Comparison

Although the initial investment cost of aluminum molds is generally lower than that of steel molds, in terms of the use value of the entire mold and the final return on investment, the advantages and disadvantages of the two still depend on the specific use conditions. All other things being equal, choosing aluminum molds can save you money on upfront tooling costs.
Repairability Comparison
A major advantage of aluminum molds is that they are easier to repair than steel molds. Due to the extreme hardness of steel, once damaged or deformed, repairing a steel mold will be an extremely difficult and costly task, and a new mold will likely need to be made. In contrast, aluminum, as a softer metal material, is easier to repair and restore even if a fault occurs during the production process.
Heating and Cooling Efficiency Comparison
Aluminum has better thermal conductivity than steel, so aluminum molds heat and cool faster than steel molds. The difference between the two can be as much as 7 times. In the injection molding production process, the time required for mold cooling occupies a large part of the entire production cycle. Appropriate selection of more efficient aluminum molds can gain significant advantages in cycle time, meaning companies can produce more products in the same time.
Comparison of Applicable Resin Types

When using advanced and complex resin formulas, steel molds have advantages over aluminum molds. While steel and aluminum are generally suitable for most standard injection molding resins, for advanced resin formulations incorporating fiberglass, other reinforcing fibers or additives, steel molds may be more suitable. Because relatively soft aluminum can be easily scratched or damaged by these additives, affecting the surface finish and texture of the product.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Aluminum Injection Molds and Steel Injection Molds
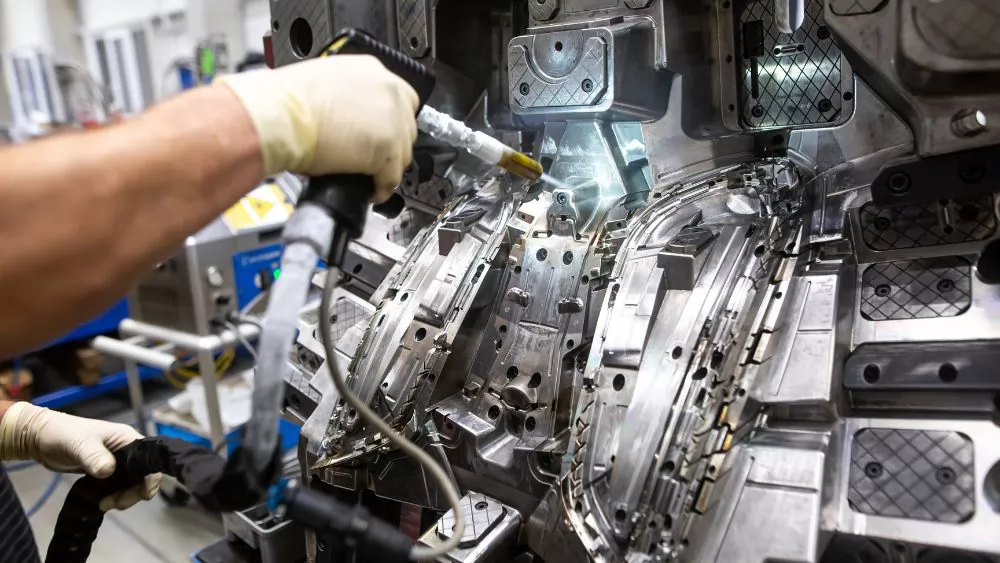

Aluminum injection molds and steel injection molds are both manufacturing tools used for injection molding, and each has some advantages and disadvantages. Here's how they compare
Aluminum Injection Mold:
Advantage:
Lightweight: Aluminum is a relatively lightweight metal, making aluminum molds easier to handle and easier to install.
Good thermal conductivity: Aluminum has good thermal conductivity, which contributes to a more uniform temperature distribution and is beneficial to the stability of the injection molding process.
Ease of processing: Aluminum is relatively easy to process and cut, so aluminum molds are relatively cheap to manufacture.
Rapid heat dissipation: Due to good thermal conductivity, aluminum molds have fast heat dissipation speed and are suitable for some injection molding applications with high heat dissipation requirements.
Shortcoming:
Lower hardness: Compared with steel, aluminum has lower hardness and is not suitable for producing large, high-precision or long-life molds.
Poor wear resistance: Aluminum has poor wear resistance and is prone to wear during long-term production. It is not suitable for high-intensity or high-frequency production.
Steel Injection Mold:
Advantage:
High hardness: Steel has relatively high hardness and is suitable for producing large-scale, high-precision and long-life molds.
Good wear resistance: Steel has strong wear resistance, is suitable for long-term and high-frequency production, and has a long service life.
High strength: Steel has superior strength and is suitable for molds that produce large, high-strength parts.
Shortcoming:
Heavy quality: Steel is relatively heavy, making the mold more bulky and not as lightweight as aluminum molds.
Poor thermal conductivity: Steel has poor thermal conductivity compared to aluminum, which can lead to uneven temperature distribution.
Choosing aluminum or steel injection molds often depends on specific production needs, including part size, production volume, service life and other factors. In some cases, composite molds of aluminum and steel can also be used to get the best of both worlds.
Aluminum Molds Vs. Steel Molds: What’s the Difference?
Aluminum molds and steel molds are two common types of injection molds, and they have some differences in materials, properties, and applications. Here are their main differences:
Material:
Aluminum mold: Mainly made of aluminum alloy, lightweight and good thermal conductivity. Common choices for aluminum alloys include 6061, 7075, etc.
Steel Molds: Typically made of tool steel, which has high hardness and strength. Common tool steels include P20, H13, etc.
| Features/materials | Aluminum mold | Steel mold |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum alloy | Steel (usually tool steel) |
| Weight | Relatively light | Relatively heavy |
| Thermal conductivity | Good thermal conductivity | Poor thermal conductivity |
| Hardness | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Relatively low | Relatively high |
| Processability | Easy to machine and cut | More difficult to machine, usually requiring cutting and grinding |
| Life | Relatively short | Relatively long |
| Surface treatment | Easy to anodize and improve surface hardness | Usually requires surface chrome plating or other treatments |
| Application areas | Small to medium-sized parts, short-run production | Large parts, long life production |
| Repeated manufacturing | Relatively easy to modify and update | Modification is difficult and usually requires re-manufacturing |
Generally speaking, the choice between aluminum molds and steel molds depends on specific production needs, including part size, production volume, service life and other factors. In some cases, you can also choose to use a composite mold of aluminum and steel to get the best of both worlds.
You Should Choose Steel Molds Under the Following Conditions

1. Steel molds are suitable for large quantities.
For molds used in high-volume and multiple-production runs, steel structures are often your best choice. There is a higher upfront investment in equipment that will last reliably for many years with proper maintenance. Over longer production runs, the strength of steel is not comparable to other materials.
2. Applicable to a variety of resins.
Although both steel and aluminum are generally suitable for a variety of standard injection molding resins, steel can offer advantages if you are working with a more complex formulation (such as one reinforced with glass, fiber, or other additives).
Relatively soft metals, such as aluminum, are at greater risk of suffering scratches or other damage from certain types of additives, which can affect the finish and texture of the final part. Make sure to check the compatibility of the resin you choose, especially if it contains additives.
3. Suitable for detailed functions
Steel molds are often Will provide better results than aluminum molds. The strength and hardness of steel means it is better able to hold its shape in those areas of extreme precision.
4. Durability
The main advantage of steel molds is that their durability far exceeds that of any other material available. If a long production period is anticipated and the mold is intended to be reused for many years, steel is the obvious choice. The higher upfront investment requires more than just a return on reuse and the tens of millions of parts the mold can produce. Steel also reduces part costs far more than any other material.
You Should Choose Aluminum Molds Under the Following Conditions
1. Aluminum molds are suitable for small batches
As mentioned above, aluminum molds can provide better value for low-volume production due to their lower upfront cost.
2. Heating and cooling time
Aluminum molds have a much higher rate of heat dissipation than steel molds, so they heat and cool much faster than steel molds, often up to 7 times. In particular, cooling time accounts for a large portion of the total injection molding cycle time. Therefore, choosing aluminum molds at the right time can significantly reduce cycle times.
3. Shrinkage, warping and other defects
Aluminum has excellent heat dissipation properties, which means the mold is better able to achieve even heating and cooling times, and faster. This has advantages in reducing the number of defective and scrapped parts.
Uneven heating and cooling are the biggest contributors to defects such as sink marks, voids, and burn marks. When used in the right application, aluminum molds can provide better cost advantages due to reduced part scrap rates.
4. Easy to modify and repair
Damaged or deformed steel forms can be difficult and costly to repair due to the material's extreme hardness. In this case, a new mold will usually be required. Aluminum molds are easier to repair and, as a softer material, are easier to modify in the event that production errors may occur.
Conclusion
As you can see, the choice between aluminum molds and steel molds depends on the specifications of your part and the project itself. You should consider the part design, the quantity you want to produce, the materials you plan to use and more to find the type of mold that is best for your product.
When you work with HingTung, we can help you make a decision quickly and easily. Our experienced team of mold designers will work hard to find the best design and materials to meet your specifications. We can work with you throughout the entire plastic injection molding process to create cost-effective, high-quality injection molding solutions for your parts. Contact us today to learn more about our capabilities and how we can handle your plastic project.