List of Contents |
Introduction: Similar at First Glance, But Different in Application
At first glance, extrusion and injection molding appear to be very similar manufacturing processes. Both processes feed molten material into machines to mass produce low-cost parts in desired shapes. Both are continuous production processes that amortize the cost as more parts are ordered. But, as we shall see, these similarities quickly disappear when looking at the differences between extrusion and injection molding.
Injection Molding Process
Injection molding is the most cost-effective method of mass producing plastic products. This plastic manufacturing process takes a plastic resin, melts it into a molten material, and injects it into a "mold tool." After cooling, the plastics manufacturer ejects the previously molten plastic material from an injection unit to form complex three-dimensional shapes with a smooth surface finish. This process can be repeated hundreds or thousands of times quickly, amortizing tooling costs and reducing costs as more plastic is ordered. Since the same mold is used for each part, and the plastic pellets used for plastic molding are very cheap, this type of plastic manufacturing is ideal for producing affordable, consistent quality parts.
Extrusion Process

The extrusion process is used to manufacture continuous linear rods. After the molten material passes through the extruder and exits the other end of the 2D die opening, it forms a rod-like shape with complex cross-sections, external shapes and even internal voids. These intricately shaped strips, often 100 or 1000 feet long, are often cut using a band saw, and can be shaped and post-modified or placed in assemblies.
Advantages of Injection Molding
Quality: Molded parts often outperform similar parts CNC machined or 3D printed from the same material.
Precision: Injection molds can be CNC machined with high precision and tolerances and produce large numbers of identical parts with tiny, intricate details.
Wide range of options: Compared to 3D printing and CNC machining, injection molding has many options for materials, colors, appearances, finishes and surface textures compared to other manufacturing processes. HingTung also provides overmolding and insert molding services with its own advantages.
Speed: Along with many other advantages, once you have a dedicated mold tool, you can produce thousands of parts with incredible speed, with a cycle time of 30 seconds or less.
Advantages of Extrusion

Metal and Plastic: Extrusion materials can be plastic and metal. Aluminum is the most common metal material, found in 80% of extruded metal parts; meanwhile, polypropylene is the most common plastic extrusion material.
Multiple methods: There are different types of extrusion, including hot extrusion, cold extrusion, and friction extrusion, each with its own unique options.
Affordable Metal Option: Metal extrusion is much less expensive than other metal processes like CNC machining, which can be much more expensive for mass production of metal parts.
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
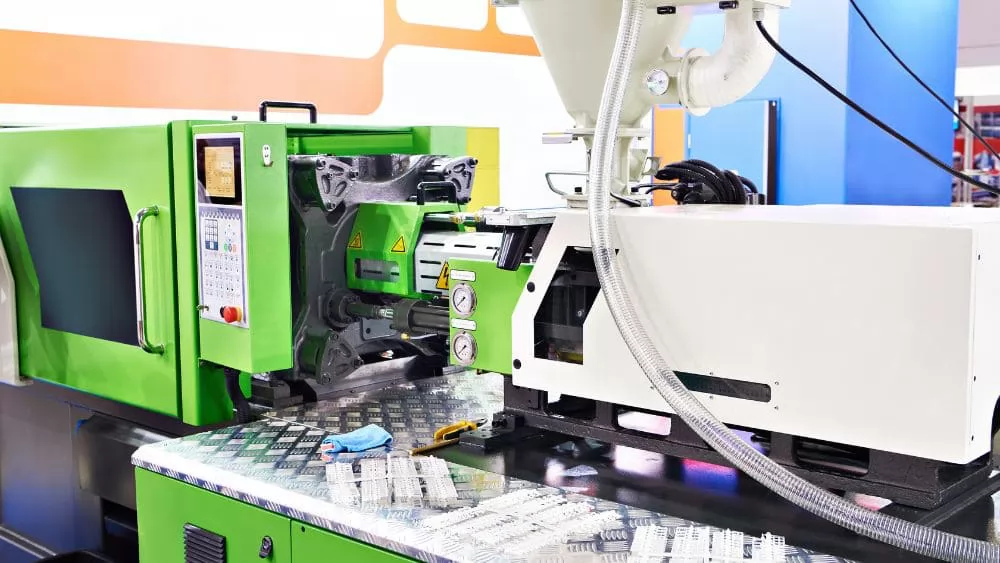

Limited Metal Production: Although metal injection molding can mass produce metal parts, most injection molding is typically used to make plastic parts.
Processing time: Plastic molding has disadvantages compared to other processes such as 3D printing. IM can be quickly replenished, but up-front tooling times extend first article lead times, meaning eD printing can potentially quickly replenish prototype parts faster than molded parts without associated tooling.
Environmental Costs: The Environmental Impact of Injection Molding requires large amounts of electricity to produce plastic products.
High upfront costs: The initial design costs for injection molding can be relatively high if the tooling costs are not compensated by ordering large quantities of plastic parts.
Disadvantages of Extrusion
Lack of complexity: Plastic extrusion methods cannot produce complex final shapes like plastic injection molding; while clamping units can help create complex cross-sections, their capabilities pale in comparison to the complexity offered by plastic molding . Of course, this lack of complexity limits the number of use cases for extrusion compared to plastic injection molding.
Environmental costs: The environmental costs of metal and plastic extrusion can be quite high, but thankfully, the industry is finding ways to reduce costs.
Fewer material choices: Extrusion has far fewer material choices than other manufacturing methods, especially injection molding.
Cost Comparison

Both processes can produce parts at a lower cost, but it should be noted that there are different cost drivers between the two methods. Injection molding tooling is expensive upfront, but this tooling can be amortized quickly, making parts very cost-effective in short order. At the same time, the extrusion process has lower upfront costs, with tooling costs 80% to 90% lower than injection molding, but over time, extrusion can be slightly more expensive because it costs a moderate amount per part. Cost to produce parts. The length of extruded rods quickly amortizes this cost.
Key Differences Between Extrusion and Injection Molding
Both methods have their own purposes and advantages, and both are valuable to plastic part manufacturers. Here, we will mainly explain the difference between extrusion molding and injection molding.
Material Fluidity
Injection molding has high requirements on material fluidity, and the material needs to be fluid enough to pass through the mold. Extrusion molding does not require as high flow as injection molding because the plastic extrusion is open and there is no huge resistance to mold reversal.
Export Expansion
The outlet expansion of extrusion molding is very obvious. This is because when the material comes out of the extrusion die, it will expand significantly due to the release of pressure. Injection molding has almost no exit swell because the material cools and solidifies immediately after filling the mold cavity during the injection molding process.
Mold Design

The molds used in extrusion molding are usually two-dimensional in shape, have low cost, and are generally used to produce simple products. The mold design for injection molding needs to consider the three-dimensional shape and is usually composed of multiple parts. The cost is higher, but it can produce precise and complex products.
Historical Differences
Among industrial producers, injection molding and/or extrusion processes are defined as the manufacture of items in various forms and sizes. Injection molding technology builds on fusion die casting technology. The jig and injection unit constitute an injection molding unit. In contrast to extrusion, injection molding produces three-dimensional structures.
In 1795, Joseph Brahman patented the first hydraulic press. However, in 1820, Thomas Burr invented the first hydraulically driven press for a manufacturing company, and the method was more thoroughly perfected. The method was not developed until 1894 for discrete extrusion of brass and metal alloys into final components. Injection molding as we know it now would eventually be born in the 1930s.
As far as plastic extrusion is concerned, this method was first used to process rubber in 1836. This is a technology in which molten plastic or various alternative materials are continuously pushed into the aperture of a two-dimensional mold by a feed screw. The molten shape is then passed through a series of templates, or blocks, which hold the correct shape as they cool.
The end result of the extrusion process has a two-dimensional shape with a continuous length. Extrusions form linear shapes that can frequently be cut to different lengths and/or slotted, punched or otherwise produced as the process runs.
Both extrusion and injection molding have advantages. One of the advantages of extrusion compared to other methods is the ability to generate complex cross-sections. Furthermore, both rigid and soft materials can be molded into any shape and the final product has a perfect surface finish compared to other technologies. There is virtually no waste in injection molding and extrusion operations, as the chips can be recycled again.
Production Efficiency and Material Utilization

Extrusion molding is a continuous production process with fast production speed and is suitable for mass production. There is less waste during the production process and the material utilization rate is high. Injection molding production speed is moderate. However, because it is an intermittent process, the production speed is relatively slow, but it is suitable for the manufacturing of high-precision products. The scrap rate is high, and waste materials such as gates and runners need to be processed, and the material utilization rate is relatively low.
Tool Differences
Injection Molding: The main tool is the injection molding machine.
Extrusion Molding: The main tool is a non-rubber extruder.
End Product Variances
Injection molding usually has a high initial design cost due to the complexity of the mold structure. On the other hand, its circular manufacturing often results in complete components that require no additional assembly or secondary machining.
Extrusion is capable of producing complex cross-sections, including multi-lumen tubes used in medical devices or food processing. Extruded materials have a flat surface and require no post-processing "cleanup".
Extrusion is suitable when a range of lengths of the same profile shape is required. By creating stock products with a continuous production chain and performing cut-to-length post-processing according to orders, setup and design costs for similar products can be minimized.
in short;
Injection molding is best for 3D product development, while extrusion is best for 2D product development.
Injection molding is the oldest method of manufacturing plastics, while extrusion is relatively new.
Extrusion can produce irregular cross-sections. Injection molding, on the other hand, may require the use of complex molds to achieve the same result.
Injection molding imparts strength to the product, but extruded products are weaker.
Injection molding is considered expensive due to high tooling costs. Nonetheless, this technique is most commonly used due to its efficiency.
Injection Molding Versus Extrusion: A Better Choice

Extrusion vs injection molding is an important debate for anyone in the plastics manufacturing industry. Unfortunately, however, there is no clear winner between the two. Both processes have their own advantages and disadvantages, but the best choice depends on the nature of the application.
The complexity of the design and the capability of the process are only part of the equation, though important considerations when choosing between molding or extrusion. However, cost requires quality, and the time available is equally important, since many projects are time-sensitive and require a perfect optimization between quality and price.
Furthermore, the two processes have a very similar scientific basis and different use cases in industrial manufacturing. The strength of injection molding is the production of complex plastics with very specific three-dimensional and high finish requirements for low tolerance dimensions. Extrusion is a less expensive process that enables two-dimensional size confinement of long continuous blocks of plastic.
In conclusion, either process is the right choice depending on the specifics of the application. Extrusion may not be possible in some cases due to the complexity of the design. However, this restriction does not apply to injection molding services. However, in many cases where cost and time are the main limiting factors, extrusion may be a viable option as it provides good quality and results more quickly.
What Materials Are Used in Both Processes?
Extrusion molding and injection molding are two common plastic molding processes that both utilize a wide range of materials, plastic resins, and polymers. There are many types of plastic resins and polymers, each with specific properties that make them suitable for a variety of different components and applications. Let’s take a look at what materials are used in each of these two processes!
There are many materials that can be used for extrusion molding. Commonly used materials include Polyoxymethylene (POM), Polypropylene (PP), Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), Polyethylene (PE), Polyamide (Nylon, PA), Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE), etc., with a wide range of material choices.
Injection molding often uses specialized materials. Material selection needs to consider its fluidity, thermal stability, etc. Commonly used materials include Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), Polycarbonate (PC), Nylon (polyamides), etc.
Application
Extrusion molding is often the preferred choice for producing plastic pipes and related products. Additionally, it is widely used for manufacturing plastic films, sheets, coatings, wire insulation, long fibers, and fibers. Some typical applications suitable for extrusion molding include straws, automotive fuel lines, gas and water pipes, window glass, glass replacement, and "bubble wrap" packaging. In contrast, plastic injection molding is ideal for mass-producing automotive components, building parts, medical tubing, containers and packaging, electronic components, food and beverage packaging, toys, bottles, and cosmetics packaging. It is particularly suitable for producing multiple parts identical to factory machinery components or engine parts, which must be precisely aligned with other parts of the machinery or engine to function properly. Furthermore, the process offers excellent versatility in handling textures, finishes, and opacity, making it the ideal choice for plastic projects requiring branding and appealing aesthetics.
HingTung: The Perfect Manufacturing Partner for All Plastic Products
Finding the right manufacturing partner can be a complicated affair. This is where HingTung comes in. With HingTung, you can get high-quality on-demand custom parts with professional prototyping and production capabilities, online instant quotes, automatic DFM analysis within seconds, and quality parts delivered within days.
If a client is unsure of a better process, HingTung's team of experts can help determine the right approach based on the specifics of the project. In addition, we offer plastic injection and extrusion mold making, overmolding and insert molding, and deal in many categories of specialty molds and various plastic finishes.
Another differentiator of HingTung is the easiest process thanks to our fully online manufacturing platform. Upload a design with other project requirements to get a quote and start the process. Afterwards, we analyze your design and create a mold flow analysis. Put the mold into production, and finally deliver the product you need to your door. The best part is that you can be 100% sure of the quality. HingTung is known for its strict quality standards and excellent results. Therefore, choosing HingTung, you can rest assured that your project will be manufactured.