When it comes to plastic molding technology, the first two that stand out that come to mind are blow molding and injection molding. But before considering or choosing any molding technique for your next project, you must consider all the important aspects and details of both processes.
Here, we take a detailed look at two molding techniques, blow molding and injection molding, and their key differences. Additionally, this blog discusses the main features and applications of both technologies. And this article also gives detailed selection suggestions, please read patiently!
Article Directory
-
3. Injection Molding vs. Blow Molding: A Detailed Comparison
3.1 Injection molding and blow molding: Product categories
3.2 Injection molding and blow molding: Complexity of products
3.3 Injection molding and blow molding: Material options
3.4 Injection molding and blow molding: Production speed
-
4. Injection Molding vs. Blow Molding: Which is Right for You?
1. What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a manufacturing technique widely used to create plastic parts and products. It is a highly versatile and efficient method for creating complex shapes with precision and consistency. During this process, the material is melted under high pressure and injected into a mold, where it cools and solidifies, eventually taking on the desired shape. Injection molding offers several advantages, including high productivity, consistent results, and a wide choice of materials. It is a popular choice across industries due to its ability to efficiently manufacture high volumes of high-quality parts.
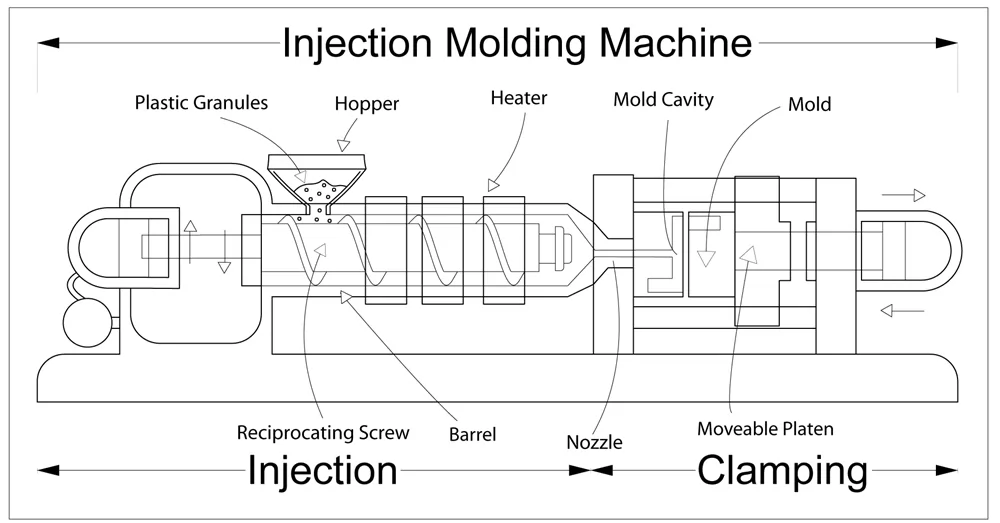
Advantages of Injection Molding
Injection molding offers efficient production with fast cycle times and high-volume capabilities, resulting in cost-effective manufacturing. It also provides design flexibility, material versatility, and consistent part quality, making it a preferred choice for producing complex shapes with precision.
-
fast and efficient production
-
Injection molding reduces cost per part
-
Ensures consistent production of the same product
-
Wide selection of materials
-
Injection molding generates minimal waste
-
Create complex shapes and intricate details
Disadvantages of Injection Molding
Notwithstanding its manifold benefits, injection molding does entail certain drawbacks. One primary disadvantage lies in the substantial initial investment required for tooling and mold design, which can prove onerous for small-scale productions. Furthermore, the process necessitates specialized equipment and skilled operators, thereby contributing to overall production costs. Another challenge manifests in the time consumed for mold fabrication, which can elongate the product development cycle. Additionally, certain materials employed in injection molding may possess limitations in terms of chemical or heat resistance.
Major Applications of Injection Molding
Injection molding finds extensive application across diverse industries. In the automotive sector, it is commonly employed for manufacturing interior trims, dashboards, and bumpers. The electronics industry relies on injection molding to produce casings, connectors, and intricate components. Medical devices, consumer goods, and packaging represent additional domains wherein injection molding is widely employed. Its capacity to yield high volumes of consistent parts with exceptional precision renders it an ideal choice for mass production.
2. What is Blow Molding?
Blow molding constitutes a manufacturing process employed for the creation of hollow plastic or glass products. It entails the inflation of heated plastic or glass material within a mold, thus taking on the desired shape. Blow molding finds common application in the production of bottles, containers, and other hollow objects characterized by specific design requirements.
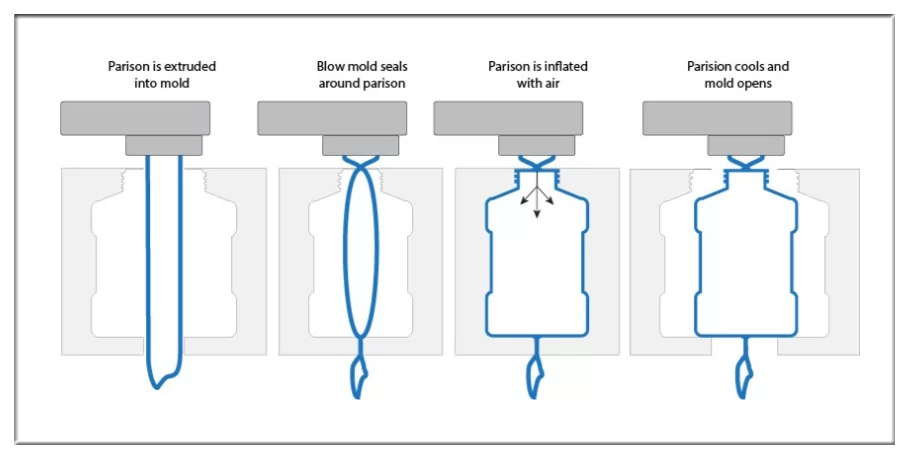
Advantages of Blow Molding
Blow molding is a manufacturing process renowned for its ability to produce seamless, lightweight, and hollow plastic products. This method involves inflating molten plastic into a mold, resulting in items characterized by uniform wall thickness, which optimizes strength-to-weight ratios. Blow molding is particularly advantageous for the high-volume production of hollow containers and packaging due to its cost-effectiveness and minimal material waste. The process also affords significant design flexibility, enabling the incorporation of handles, closures, and other features, thereby expanding its applicability across various industries.
Beyond these core benefits, blow molding often presents lower tooling costs compared to alternative molding techniques. Coupled with its capacity to create intricate shapes using a single mold, this process can yield substantial cost reductions. Moreover, blow molding is amenable to automation, thereby enhancing production efficiency and reducing labor expenditures.
Disadvantages of Blow Molding
While blow molding boasts its advantages, it also carries certain limitations. One notable drawback pertains to its confinement to hollow products, limiting its scope when compared to injection molding. The process may also encounter challenges in achieving high precision and intricate details. Another disadvantage involves the restricted range of materials suitable for blow molding, primarily focusing on thermoplastics. Furthermore, the initial tooling and mold costs for blow molding can surpass those associated with other manufacturing methods.
Main Applications of Blow Molding
Blow molding finds significant utilization in industries such as packaging, beverages, and consumer goods. It is widely employed for producing plastic bottles, containers, and jugs intended for liquid storage. The food industry employs blow molding in the manufacturing of packaging materials like jars, trays, and tubs. In the automotive sector, blow molding is commonly used for fabricating fuel tanks and ducts. Additionally, it finds application in the production of toys, household products, and industrial components.
3. Injection Molding vs. Blow Molding: A Detailed Comparison
This video goes over the differences in injection molding & blow molding. Watch this video to learn more.
| Injection Molding | Blow Molding | |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Injecting molten material into a mold to create solid objects. | Inflating heated material inside a mold to create hollow objects. |
| Product Type | Solid objects | Hollow objects |
| Complexity | Can produce complex and intricate shapes with high precision. | Limited to simpler shapes and designs. |
| Material Options | Wide range of materials including plastics, metals, and composites. | Primarily focuses on thermoplastics. |
| Production Speed | Fast production cycle times | Slower production cycle times |
| Tooling Cost | High initial tooling and mold design cost. | Lower tooling cost compared to injection molding. |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for large-scale production runs. | Cost-effective for producing large quantities of hollow objects. |
| Applications | Automotive, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, and more. | Packaging, beverages, containers, and toys. |
3.1 Injection molding and blow molding: Product categories
Injection Molding: This process excels at producing a vast array of solid plastic products characterized by intricate details and complex geometries. Applications span across industries, including automotive components, electronics, medical devices, consumer goods, and industrial parts. Injection molding is ideal for creating products with precise tolerances and consistent dimensions.
Blow Molding: Primarily used for manufacturing hollow plastic products, blow molding is particularly well-suited for containers, bottles, tanks, and other similar items. Its ability to create seamless, uniform wall thickness makes it a popular choice for packaging applications.
3.2 Injection molding and blow molding: Complexity of products
Injection Molding: This process is capable of producing highly complex parts with undercuts, fine details, and varying wall thicknesses. The intricate nature of the molds used in injection molding allows for the creation of products with sophisticated features.
Blow Molding: While blow molding can produce products with basic shapes and some degree of complexity, it is generally better suited for simpler, hollow designs. The process is limited in its ability to create intricate internal features or undercuts.
3.3 Injection molding and blow molding: Material options
Injection Molding: Offers a broader range of material compatibility, including thermoplastics, thermosets, and engineering plastics. This versatility allows for the production of parts with varying properties, such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance.
Blow Molding: Primarily focuses on thermoplastics due to their ability to be heated and inflated. However, the range of materials suitable for blow molding is narrower compared to injection molding.
3.4 Injection molding and blow molding: Production speed
Injection Molding: Typically offers higher production speeds due to the automation involved in the process. Cycle times can be relatively short, making it efficient for high-volume production.
Blow Molding: While production speeds have improved with technological advancements, the process generally tends to be slower than injection molding, especially for larger or more complex products.
3.5 Injection molding and blow molding: Processing costs
Injection Molding: Often involves higher upfront costs due to the complexity of molds and tooling. However, production costs per unit can be lower for high-volume production runs.
Blow Molding: Generally has lower tooling costs compared to injection molding, making it a more cost-effective option for lower production volumes. However, the cost per unit can increase for larger or more complex products.
3.6 Injection molding and blow molding: Cost-effectiveness
Injection Molding: Offers excellent cost-effectiveness for high-volume production of complex parts with consistent quality. The initial investment in tooling is typically recovered through economies of scale.
Blow Molding: Provides a good balance of cost and production efficiency for hollow products. It is particularly cost-effective for high-volume production of standard containers and bottles.
4. Injection Molding vs. Blow Molding: Which is Right for You?
The selection of injection molding or blow molding as a manufacturing process is contingent upon a product's specific attributes, including its geometry, complexity, and intended application. Injection molding excels in producing intricate, solid parts characterized by high precision and dimensional accuracy. This process is commonly employed in sectors such as automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
Conversely, blow molding is optimized for the production of hollow, lightweight components with uniform wall thickness. Industries reliant on packaging, beverage containers, and consumer goods frequently leverage this process.
To make an informed decision, manufacturers must carefully consider factors such as production volume, cost, design flexibility, and material compatibility. Consulting with manufacturing experts or mold designers can provide valuable insights into selecting the most appropriate process for specific product requirements. Ultimately, the optimal choice between injection molding and blow molding necessitates a thorough evaluation of a product's unique characteristics and production objectives.

6. Best Injection Molding Service Company in China
With more than 10 years of experience in plastic molding, Hing Tung Mold is an excellent injection molding manufacturer serving various industries such as automotive, electronics, electrical appliances, etc. We provide comprehensive services in the field of plastic injection molding as well as high-quality custom plastic injection molds.
We are able to perform injection molding part design, injection molding prototyping, precision injection mold making and plastic injection molding at reasonable cost and short lead time. Contact us today to find out about China Injection Molding costs and get your job done with ease!
Conclusion
In conclusion, injection molding and blow molding represent distinct manufacturing processes, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Injection molding is suitable for fabricating solid objects boasting intricate shapes, while blow molding is ideal for creating hollow products with consistent wall thickness. The selection between the two processes hinges upon factors such as product design, volume requirements, cost considerations, and material compatibility. By comprehending the disparities between injection molding and blow molding, manufacturers can make well-informed decisions to achieve desired product outcomes.
Related content recommendation
- Everything You Need to Know About China Injection Molding Services
- Die Casting Vs Injection Molding: What are Their Main Differences?
- Plastic Injection Molding: A Comprehensive Guide
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Molding Process
- 3D Printing VS Injection Molding: Which Is The Better Choice?