No matter what product you purchase, you are investing in equipment. The equipment you trust is built to last. So when you’re narrowing down your options with return on investment in mind, it’s important to weigh the advantages of plastic injection molding versus rotational molding (or rotational molding) manufacturing processes.
Table of Contents
- What is rotational molding?
- What is injection molding?
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotational molding and injection molding?
- Injection molding vs rotational molding: Which process wins?
- What are the applications of injection molding and rotational molding?
- How to choose the right plastic product for your application
- Learn about injection molding and rotational molding from HingTung
What is rotational molding?
Rotational molding is a thermoplastic processing method commonly used to create large, simple-shaped plastic products. The process involves heating plastic pellets to a plastic state and then passing the molten plastic through a rotating mold to coat the surface of the mold. Because the mold rotates while also moving in other axial directions, it ensures that the plastic coated on the mold surface is evenly distributed. This is then cooled and solidified to form the final product.
What is injection molding?
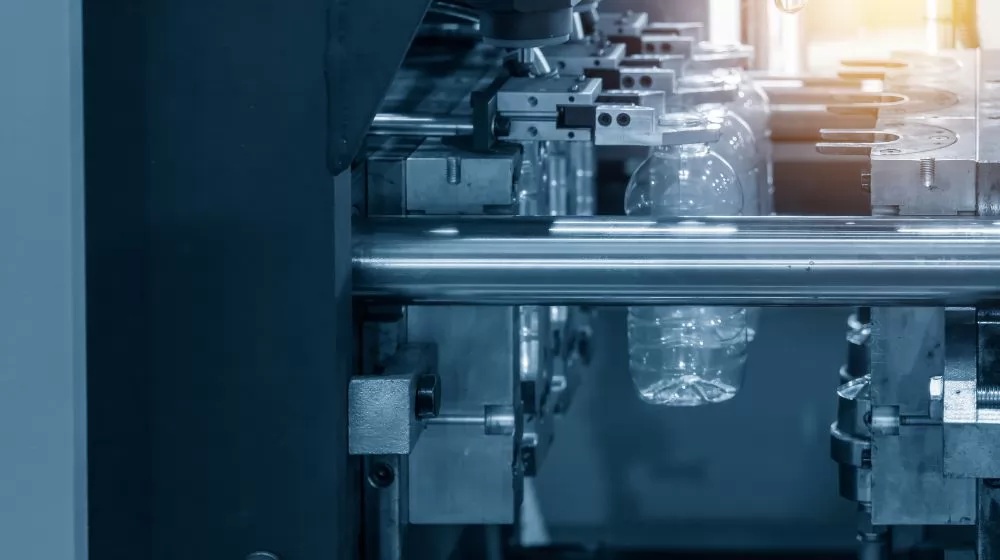

Injection molding is a common plastic processing process suitable for producing plastic products of various sizes and shapes. The process involves heating plastic pellets to a molten state and then injecting the molten plastic into a metal mold. A mold usually consists of two parts that, when closed, form the shape of the final product. Through a high-pressure injection system, the plastic fills the entire mold cavity, then cools and solidifies, finally forming a plastic product.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of rotational molding and injection molding?
Advantages and disadvantages of rotational molding:
advantage:
Suitable for large products: Rotational molding is suitable for manufacturing large, simple-shaped, thin-walled or hollow plastic products, such as sinks and storage bins.
Low-cost tooling: The tooling cost of rotational molding is relatively low and suitable for small batch production and customized products.
Lower processing temperatures: Since extremely high processing temperatures are not required, rotational molding is more suitable for certain low melting point plastics.
shortcoming:
Slower production speed: Compared with injection molding, rotational molding has a slower production speed and is less suitable for mass production.
Limitations of complex geometries: For complex geometries, rotational molding has relatively poor adaptability.
Relatively low surface quality: Due to the natural process of coating, the surface quality of rotational molding may not be as high as that of injection molding.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Molding:
advantage:
High production efficiency: Injection molding is suitable for mass production and has high production efficiency.
High precision and surface quality: Injection molding is capable of producing plastic products with high precision and good surface quality, suitable for various industrial and consumer goods fields.
Widely applicable to different plastics: Injection molding has strong adaptability to a variety of plastic materials, including high-temperature, high-strength and high-toughness plastics.
shortcoming:
High tooling costs: The cost of making and customizing injection molds is relatively high, which can be a burden during the initial investment phase.
Not suitable for large products: Injection molding is not suitable for manufacturing large products, especially those with hollow structures.
Limited Design Flexibility: Injection molding can have some limitations when it comes to handling complex geometries, especially when it comes to mold making cycles.
Injection molding vs rotational molding: which process wins?
1. Product type and size:
Injection molding: Suitable for producing small to large, precision parts, especially with high efficiency in mass production.
Rotational molding: More suitable for large, simple-shaped, thin-walled or hollow products, such as sinks and storage boxes.
2. Manufacturing cost:
Injection Molding: High tooling costs, but in mass production, unit costs are relatively low.
Rotational molding: Tool costs are relatively low and suitable for low-volume production and customized products.
3. Production efficiency:
Injection molding: Suitable for mass production with high production efficiency and precision.
Rotational Molding: Slower production speed, more suitable for small batches and specific products.
4. Material adaptability:
Injection molding: It has strong adaptability to a variety of plastic materials and can handle plastics with high temperature, high strength and high toughness.
Rotational molding: More suitable for plastics with low melting point and good fluidity.
5. Design flexibility:
Injection molding: High design flexibility and suitable for producing complex geometries, but the mold production cycle is long.
Rotational molding: Very adaptable, but has some limitations when dealing with complex geometries.
The choice between injection molding or rotational molding depends on specific product requirements, production scale, design complexity, and budgetary considerations. In practical applications, it is usually necessary to comprehensively consider the above factors according to the specific conditions of the project to determine the most suitable plastic molding process.
What are the applications of injection molding and rotational molding?
Injection molding applications:
Electronics industry: Manufacture of electronic components and housings, such as connectors, sockets, plastic shells, etc.
Automobile industry: Produces automobile parts, including dashboards, door panels, lamps and interior parts.
Medical field: Produces medical equipment and appliances, such as syringes, medical device casings, etc.
Home furnishings: Manufactures a variety of home products such as chairs, tables, containers, toys, etc.
Packaging industry: Produces plastic packaging containers, bottles, boxes, etc.
Consumer products: Including plastic products such as toothbrushes, cosmetic containers, tableware, etc.
Industrial use: Manufacture of various industrial parts, such as pipe connectors, valves and plastic gears.
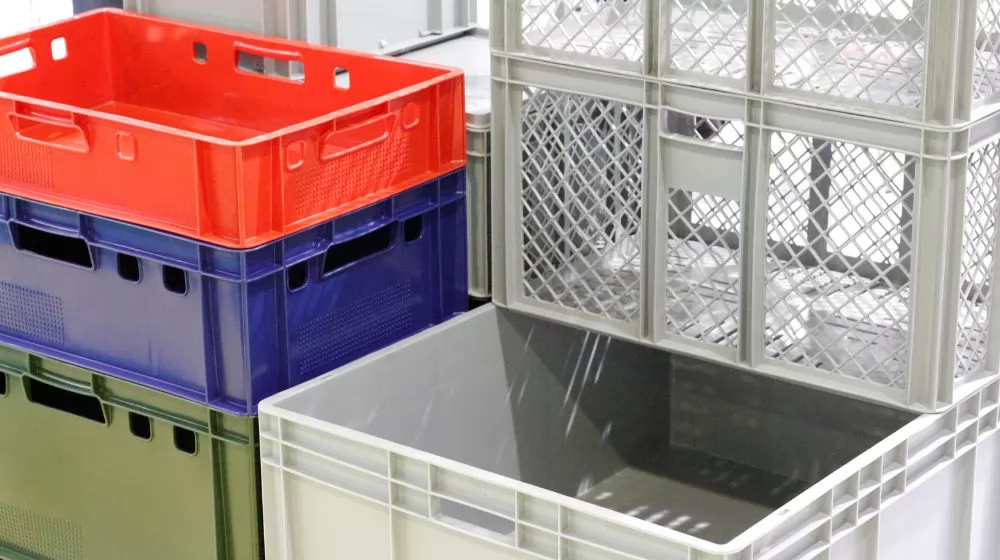

Applications of rotational molding:
Sinks and containers: Produces large sinks, storage bins, buckets and other containers.
Amusement facilities: Manufacture of outdoor toys, slides, playground equipment, etc.
Construction field: Producing large-scale building components, such as building materials, decorative components, etc.
Vehicles: Produces hulls, dinghy and other hulls for watercraft.
Gardening supplies: Manufacture of flower pots, garden tool boxes, gardening equipment, etc.
Agricultural field: Produces agricultural equipment, such as water tanks, feed boxes and agricultural storage boxes.
Entertainment equipment: Manufacturing of large-scale entertainment equipment, skateboard ramps, etc.
These are some typical applications of injection molding and rotational molding in different fields. Selecting the appropriate molding method often depends on the size, shape, quantity and material requirements of the product.
How to choose the right plastic product for your application

There are several factors to consider when choosing the right plastic product for your application, here are some suggestions:
1. Application requirements
Mechanical properties: Based on the requirements of the application, select the appropriate plastic to meet the required mechanical properties, such as strength, hardness, wear resistance, etc.
Chemical properties: Consider the corrosion resistance and chemical stability of the plastic in a specific chemical environment.
2. Temperature requirements
Temperature Resistance: Select the plastic based on the application's operating temperature range to ensure stable performance under the required temperature conditions.
3. Physical properties
Density and weight: Consider the density and weight of the product to select the appropriate plastic to meet design requirements.
Conductivity: When conductive properties are required, choose plastics with conductive properties.
4. Manufacturing process
Processability: Consider the processability of the plastic, including molding, injection molding, extrusion and other processes, to ensure it is suitable for your production process.
5. Environmental protection and sustainability
Recyclability: If environmental protection is a key factor, choose recyclable plastic materials.
Biodegradability: Consider using biodegradable plastics to reduce environmental impact.
6. Cost considerations
Raw Material Cost: Consider the cost of plastic raw materials and match it with your budget.
Production process cost: Consider the cost of the manufacturing process, including mold making, processing and post-processing.
7. Standards and Regulations
Comply with standards: Make sure the plastic you choose complies with applicable industry standards and regulations.
8. Durability and lifespan
Weather Resistance: Consider weather resistance when used outdoors or in harsh environments.
Life expectancy: Choose a plastic with appropriate durability based on the product’s life expectancy.
When selecting plastic products, it is best to conduct adequate research and testing, and it is necessary to work with the material supplier to ensure that the selected material meets the needs and requirements of the specific application.
Learn about injection molding and rotational molding from HingTung
HingTung is an injection molding manufacturer with over 13 years of experience. So if you are a designer looking for the best ways to manufacture plastic products, we invite you to contact us. We have extensive experience in the field of injection molding and are committed to providing you with high-quality, customized plastic product production services. We look forward to working with you to realize your design vision.