Plastic is the most widely used material today due to its high adaptability and low cost. Currently, there are viable options for producing plastic parts such as 3D printing, CNC machining, polymer casting and extrusion.
Plastic injection molding and thermoforming are two plastic processing methods that are widely used in various industries. Choosing between plastic thermoforming or injection molding may have been relatively straightforward in the past, but as manufacturing technology advances, product requirements increasingly conflict with the capabilities of these two methods.
As important methods in the plastics processing industry, thermoforming and injection molding play a vital role in the production of plastic parts. This article will focus on the advantages of both approaches and analyze the circumstances under which one is more appropriate.
Article Directory:
-
What are the main differences between injection molding and thermoforming?
-
What are the mutual alternatives of injection molding and thermoforming?
-
What are the similarities between injection molding and thermoforming?
-
What are the main fields of application for injection molding and thermoforming?
-
What are the advantages of injection molding compared to thermoforming?
What is thermoforming?
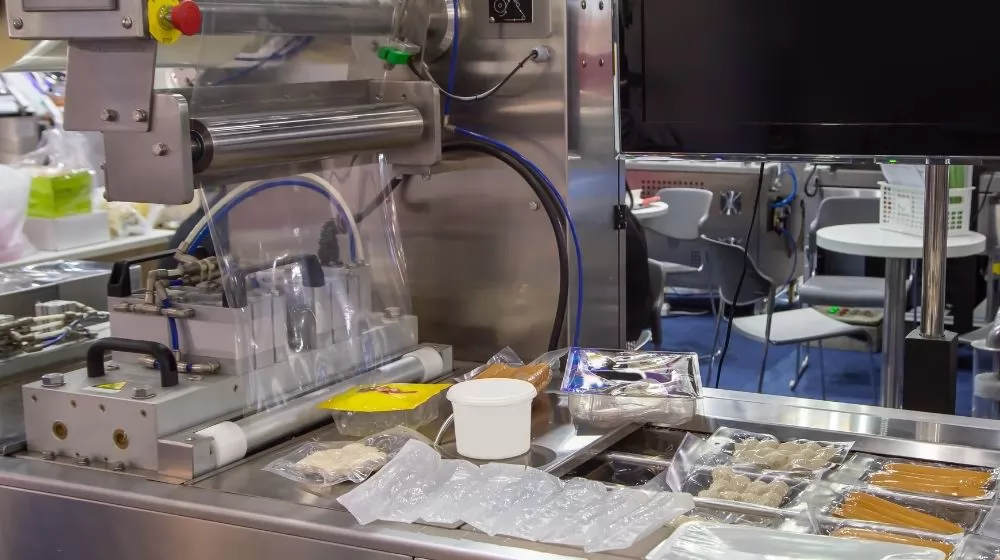

Thermoforming is a manufacturing process typically used to process materials such as plastics. In thermoforming, the material is heated to a plastic state and then placed in a mold where it is given the desired shape by pressure or vacuum. Once the material cools and solidifies, it will retain the shape it was molded into.
There are several common methods of thermoforming, including:
Blister molding: The heated plastic sheet is adsorbed to the mold with the desired shape, and then adhered to the surface of the mold by vacuum or air pressure.
Compression molding: A heated plastic sheet is placed in a mold and pressure is used to mold it into the shape the mold requires.
Hot-melt molding: Plastic particles are heated and melted and injected into the mold, and formed into the desired shape after cooling.
Hot blow molding: Heated plastic is extruded into a tube, which is then blown by air pressure into the shape of a mold.
Thermoforming is widely used in the manufacture of various plastic products such as packaging containers, plastic tableware, automotive interior parts and toys. This manufacturing process enables the rapid and economical production of complex shapes in high volumes.
What is injection molding?
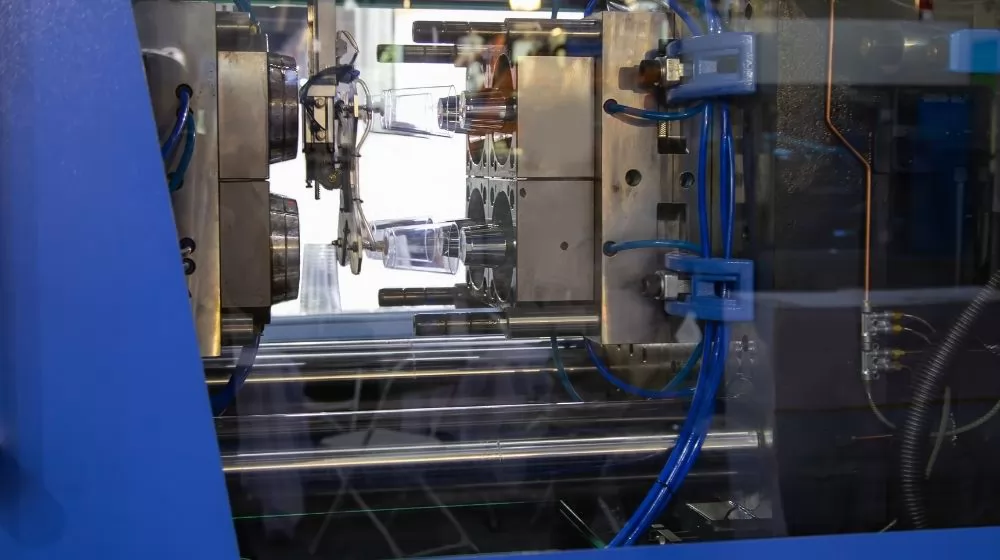

Injection molding is a common plastic processing process used to produce a variety of plastic products. In the injection molding process, heated and molten plastic pellets are injected through an injection machine into a closed mold and then filled to the shape of the mold under high pressure. Once the plastic has cooled and hardened, the mold is opened and the formed plastic product is removed.
Injection molding is usually divided into the following steps:
Raw material preparation: Put plastic granules or powder into the hopper of the injection machine to prepare the raw materials for injection molding.
Heating and melting: The injection machine heats and melts the raw material to make it into a plastic state.
Injection injection molding: Molten plastic is injected into the closed mold through the injection system of the injection machine. Molds usually contain the shape of the desired product.
Mold filling and cooling: After the plastic fills the shape in the mold, it begins to cool and harden.
Mold opening: Once the plastic has cooled sufficiently, the mold is opened and the formed plastic product is removed.
Injection molding is widely used in various industries to produce a wide variety of plastic products, such as plastic parts, containers, toys, electronic product casings, etc. The advantages of this process are high efficiency, high precision, and the ability to mass-produce plastic products in a short period of time. The continuous development of injection molding technology also provides more possibilities for the quality and design of plastic products.
What are the main differences between injection molding and thermoforming?
Processing method:
Injection molding: In the injection molding process, after the plastic pellets are heated and melted, they are injected into a closed mold through an injection machine and filled with the shape of the mold under high pressure. After the plastic cools, the mold is opened and the formed plastic product is taken out.
Thermoforming: The process of thermoforming is to heat the plastic to a plastic state, apply pressure or vacuum force to the surface of a mold, and maintain the desired shape after cooling.
Process features:
Injection molding: suitable for the production of large-volume, relatively complex plastic products, such as electronic product casings, auto parts, etc. The forming process is fast and precise, enabling high production efficiency.
Thermoforming: suitable for the production of thin-walled plastic products, such as plastic cups, boxes, packaging containers, etc. Compared with injection molding, thermoforming is more flexible in the production process and can adapt to more diverse shape requirements.
Product characteristics:
Injection Molding: Because the plastic is filled into the mold shape under high pressure, the molded plastic product is denser and usually better in strength and hardness.
Thermoforming: Thermoformed products are relatively thin and have low density, so the strength and hardness may be relatively low, but it is suitable for some lightweight products.
Cost of production:
Injection molding: usually requires high equipment investment and mold manufacturing costs, but for mass production, the production cost of a single product is low.
Thermoforming: The investment in equipment is low, and the cost of manufacturing molds is relatively low. It is suitable for small batch production, but the production cost of a single product may be high.
What are the mutual alternatives of injection molding and thermoforming?
Injection molding and thermoforming can be substituted for each other in some specific cases, depending on product demand and production scale. Some of their mutual substitutes are as follows:
Blister molding: Blister molding is a variant of thermoforming that can replace injection molding in some cases. Blister molding works by heating a plastic sheet and sucking it onto a mold with the desired shape, then applying vacuum or air pressure to conform it to the surface of the mold. Blister molding is suitable for the production of thin-walled plastic products, such as packaging containers, envelopes, etc.
3D printing: In some cases, 3D printing technology can replace traditional injection molding and thermoforming processes. 3D printing is a manufacturing method that adds materials layer by layer, and can directly generate products of the desired shape based on the CAD model. It is especially suitable for the production needs of low-volume customization, but it may not be cost-effective for large-scale production.
Compression Molding: Compression molding is a process similar to thermoforming that can be used as an alternative to some injection molding applications. Compression molding works by placing a heated sheet of plastic in a mold and then using pressure to mold it into the shape the mold requires. It is suitable for the production of thicker plastic products, such as plastic sheets, thin-walled containers, etc.
Rotational molding: Rotational molding is a special thermoforming process, suitable for the production of hollow plastic products, such as toys, seats, etc. It heats and rotates the mold so that the plastic covers the mold evenly to form a hollow molded product.
It is necessary to select suitable substitutes according to specific product design requirements, production scale and budget. Each process has its characteristics and scope of application, and choosing an appropriate process can better meet production needs.
What are the similarities between injection molding and thermoforming?

As two plastic processing techniques, injection molding and thermoforming have some similarities, which are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
Material processing: Whether it is injection molding or thermoforming, they require heating the plastic material to a plastic state so that it can be shaped. The heated plastic forms the desired product shape after cooling under the action of the mold.
Product shape control: Whether it is injection molding or thermoforming, the shape of the final formed product is determined by the mold. The mold is made according to the product design requirements to ensure the accurate shape of the finished product.
Wide range of uses: Both injection molding and thermoforming can be used to produce a variety of plastic products, such as packaging containers, parts, toys, etc. They are all commonly used processes in plastic processing and are widely used.
Mass production: Whether injection molding or thermoforming, they are suitable for mass production. These two processes can efficiently produce a large number of products of the same or similar shape in a short period of time.
Process control: Both injection molding and thermoforming require strict control of process parameters such as heating temperature, injection pressure, and cooling time to ensure the quality and dimensional stability of the finished product.
Although injection molding and thermoforming have similarities, they still have some differences in processing methods, scope of application and some specific applications. Choosing the right process depends on the specific product design and production needs.
What are the main fields of application for injection molding and thermoforming?
Injection molding and thermoforming are common plastic processing processes, and they have a wide range of applications in different application fields, as follows:
The main application areas of injection molding include:
Electronics and electrical appliances industry: production of electronic product casings, sockets, connectors and other plastic parts.
Automotive industry: Manufacture of auto parts such as dashboards, lights, door handles, etc.
Packaging industry: production of plastic bottles, plastic boxes, food packaging, etc.
Daily necessities and household items: production of plastic chairs, plastic buckets, plastic dishes, etc.
Medical Devices: Manufacturing of plastic parts for medical appliances and devices.
The main application areas of thermoforming include:
Packaging industry: producing plastic cups, plastic boxes, plastic trays and other packaging products.
Manufacturing: production of plastic sheets, thin-walled containers, foam plastic products, etc.
Toy industry: Manufacture of plastic toys, game accessories, etc.
Daily necessities and household items: production of plastic tableware, plastic pots, plastic cups, etc.
Construction industry: production of plastic sheets, plastic pipes, and plastic products for interior decoration, etc.
It should be noted that although injection molding and thermoforming overlap in some applications, they are more suitable for different product types and production scales due to their different processing methods and characteristics. According to specific product needs and production requirements, choosing the right process can improve production efficiency and product quality.
What are the advantages of injection molding compared to thermoforming?
High production efficiency: Injection molding is suitable for large-scale production. The injection molding machine can realize automatic production and can produce multiple products per minute, so the production efficiency is high.
High production precision: The design and manufacture of injection molding molds are relatively precise, which can produce highly consistent products with good dimensional and shape stability.
Suitable for complex shapes: Injection molding can produce complex shapes and details, and is suitable for the production of complex plastic products, such as automotive parts, electronic product casings, etc.
Wide selection of materials: Injection molding can process many different types of plastic materials, such as polypropylene, polyethylene, ABS, etc., so it has high flexibility in material selection.
Good production stability: During the injection molding process, the plastic is filled in the mold under high pressure, and the finished product has uniform density, good strength and hardness, and high product stability.
Less waste of plastic: In the process of injection molding, the amount of materials used can be controlled to avoid waste and improve the utilization rate of materials.
In general, injection molding is suitable for mass production of plastic products with complex shapes, and has high production efficiency and product quality stability. However, it needs to be considered that the investment in injection molding equipment is high, and the mold manufacturing of specific products may also increase the initial cost. Selecting an appropriate process also needs to comprehensively consider factors such as product requirements, production scale and economic benefits.
Which technology is right for you?

For certain industries and applications, both processes can be used to make plastic parts. But many industries turn to specific approaches based on the unique attributes of the project at hand. In order to determine which process is best for your plastic molding job, it is important to carefully evaluate the unique characteristics and requirements of your project.
Injection molding is best used for most projects that require higher throughput, very complex or detailed designs, short lead times, or automated programming to reduce manufacturing costs. The injection molding process can meet all of these requirements to accurately produce high-volume high-precision parts in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Alternatively, thermoforming is ideal for projects requiring smaller production quantities, lower tooling costs, or parts with color and texture. For large parts with simplified designs, thermoforming offers short lead times and a wide range of aesthetic options.
Both methods ensure outstanding reliability and high quality, whether you are working with plastic pellets for injection molding or plastic sheets for thermoforming. The best choice for a particular job will depend on the unique requirements of the current application.
Conclusion
Both thermoforming and injection molding are important plastic processing methods, each suitable for different scenarios and needs. Choosing the best method requires comprehensive consideration of factors such as product shape, production batch size, cost, and production cycle, and making wise decisions based on actual conditions. With the continuous advancement of technology, manufacturers and designers will have more flexible and diverse choices to meet changing market needs.
HingTung is proud to be one of the world's leading plastic injection molding service providers. Please contact us to get high quality service at the most affordable price.