A plastic injection molding machine is a manufacturing tool used for producing plastic parts by injecting molten material into a mold. This process allows for high-volume production of plastic components with great precision and repeatability.
Discover how this pivotal machinery revolutionized the manufacturing industry, shaping the world around us through the objects it creates. Read on to unlock the intricate workings of injection molding machines and their substantial impact on product development.
What is a Plastic Injection Molding Machine?
A plastic injection molding machine is a manufacturing tool used for producing plastic parts by the injection molding process. It consists of two main components: an injection unit and a clamping unit. The machine functions by melting plastic granules until they are in a liquid state and then injecting them into a mold where they solidify into the final product. This technology enables high-volume production of plastic parts with consistent quality and intricate shapes that would be difficult or economically unfeasible to produce by other methods.
How do plastic injection molding machines work?
Plastic injection molding machines are designed to produce various plastic parts by injecting molten plastic material into a mold. The process begins with feeding plastic pellets into the machine’s hopper. These pellets move towards the barrel of the machine where they are heated to their melting point. Next, a screw inside the barrel, which can both rotate and move forward, mixes and pushes the now viscous plastic toward the nozzle at the end of the barrel.
Once enough molten plastic accumulates in front of the screw, the injection process starts. The screw moves forward to inject the melted plastic through the nozzle and into a mold cavity that is shaped as per the required part design. Pressure is applied to ensure all cavities within the mold are filled with material.
After filling, there is a cooling phase; during this time, the molten material solidifies and takes on the shape of its container—the detailed features of a molded product are created here. Once cooled sufficiently, a mechanism separates both halves of mold apart along its-parting line. The finished piece is ejected from the mold by ejector pins or rods while also being assisted by air blasts or robotic arms in some cases.
Finally, after ejection, any required post-processing such as trimming excess material (known as flash) or painting is done before final inspection of produced units—ensuring quality and conformance to specifications.
Types of Injection Molding Machines
Injection molding machines are categorized primarily into three types: hydraulic, electric, and hybrid. Each type offers unique advantages and can be selected based on the specific requirements of the manufacturing process.
Hydraulic Plastic Injection Molding Machine Hydraulic injection molding machines have been the traditional workhorses of the plastic industry. These machines use hydraulic systems to generate the clamping force needed to hold the mold in place during injection and cooling. They are known for their ability to produce large clamping forces, making them suitable for producing large and complex parts.
Electric Injection Molding Machine Electric injection molding machines utilize servo motors for both the injection and the clamping units, ensuring highly accurate control over the process with energy-saving benefits. These machines provide faster cycle times and require less maintenance compared to their hydraulic counterparts. Electric machines are typically more precise, offering better repeatability which is crucial for producing high-tolerance parts.
Hybrid Injection Molding Machine The hybrid injection molding machine combines elements of both hydraulic and electric technologies. In a hybrid setup, a servo motor might drive some portions of the machinery that require precise movements, whereas hydraulics would facilitate components requiring raw power. The goal with hybrids is to take advantage of the best features from both electric and hydraulic designs — precision from electric systems with power from hydraulics — potentially creating a cost-effective yet high-performance alternative.
|
Type |
Description |
Advantages |
|
Hydraulic |
Uses hydraulic system for movement; Suited for larger, more intricate parts |
Great clamping force; Robust design |
|
Electric |
Utilizes servo motors; Offers precision control; Energy-efficient |
High precision; Fast cycle times; Low maintenance |
|
Hybrid |
Combination of hydraulic and electric systems |
Cost-effective; Good balance between precision and power |
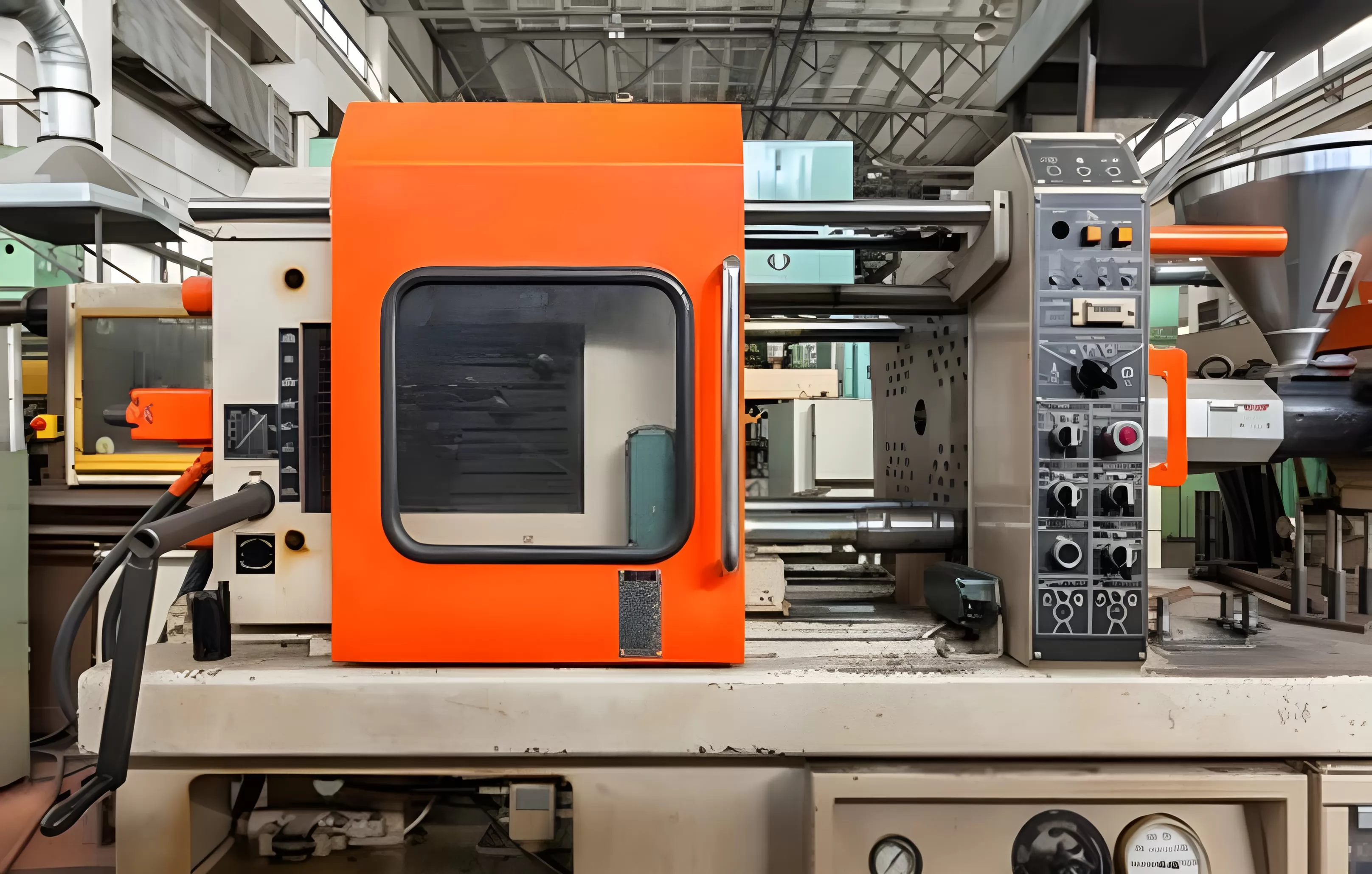
1.Hydraulic Plastic Injection Molding Machine
Hydraulic plastic injection molding machines are a prevalent choice in the industry, known for their powerful clamping force and ability to process various materials. These machines utilize hydraulic systems to generate the requisite force for clamping and injection processes. The core of this system includes pumps, hydraulic fluids, and cylinders that work collectively to move the machine's components.
A primary advantage of hydraulic machines is their robustness and capability to produce large volumes of parts while maintaining consistent quality. They offer excellent control over clamping pressure, which is critical for manufacturing complex parts. However, it should be noted that these machines traditionally consume more energy compared to electric or hybrid variants due to continuous pump operation.
When discussing maintenance, hydraulic injection molding machines require regular checks on the hydraulic system to ensure there are no leaks and that the fluid is clean. Maintaining these aspects ensures smooth operation and longevity of the machine.
It’s also pertinent to acknowledge that advances in technology have allowed newer models of hydraulic injection molders to become more energy-efficient than older generations, through variable displacement pumps or servo-driven hydraulics which scale operational output according to real-time demand.
|
Feature |
Detail |
|
Operation |
Utilizes hydraulic systems for clamping and injection |
|
Clamping Force |
Powerful; excellent control |
|
Material Processing |
Capable of processing a wide variety of materials |
|
Production Volume |
Suitable for high-volume production |
|
Energy Consumption |
Higher compared with electric/hybrid models |
|
Maintenance |
Regular checks required for the hydraulic system |
|
Technological Advancements |
More energy-efficient models available with modern technology |
|
Suitability |
Ideal for manufacturing complex parts consistently at large volume |

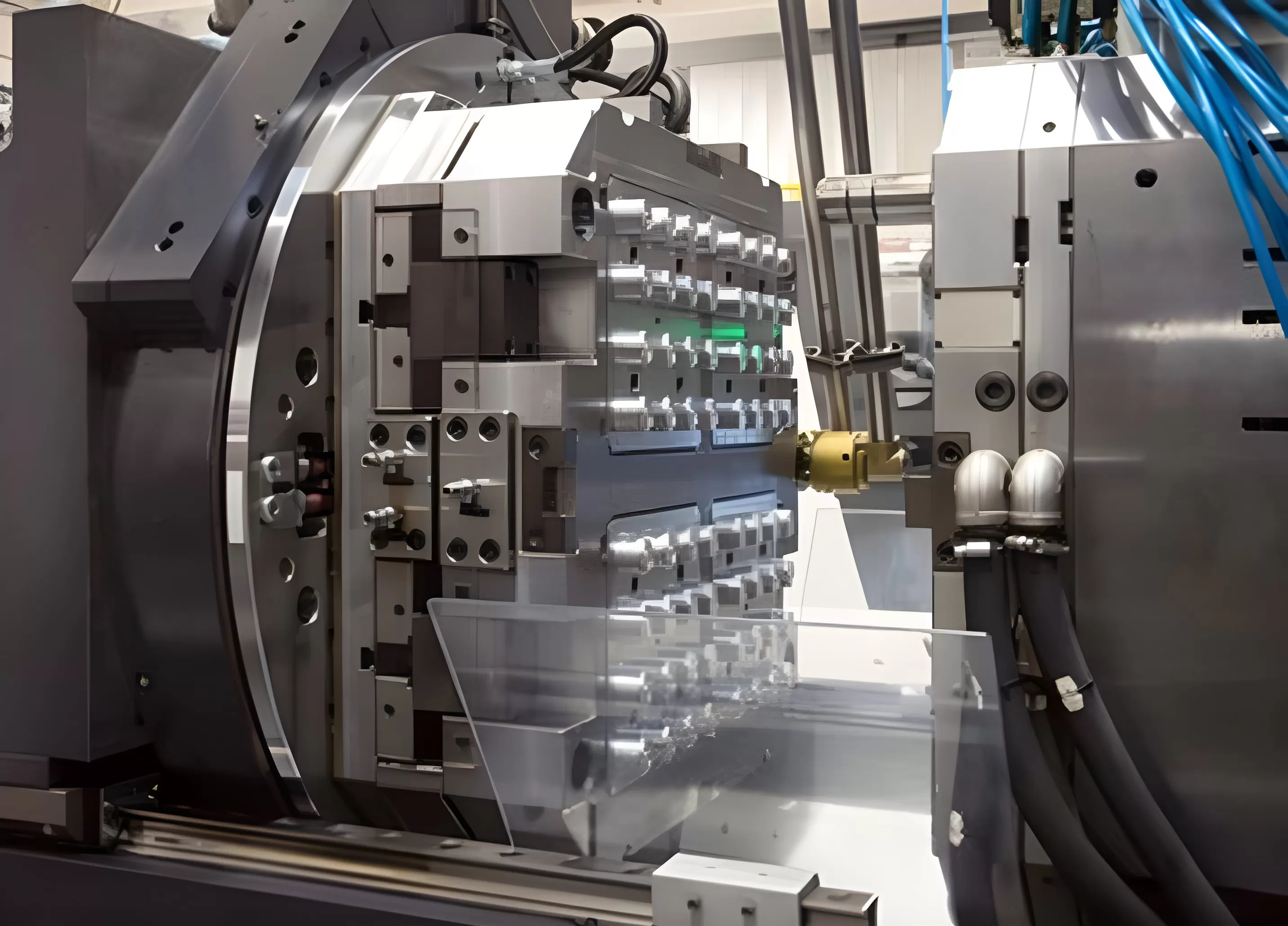
2.Electric Injection Molding Machine
Electric injection molding machines are a modern alternative to traditional hydraulic models, powered solely by electricity. These machines are known for their precision, repeatability, and energy efficiency. Without the need for hydraulic oil, they operate more cleanly, reducing the chances of product contamination. Electric injection molding machines utilize servo motors to drive all of the machine's movements, providing extremely accurate control over the process. The use of servomotors allows for reduced cycle times as well as saving energy compared to their hydraulic counterparts.
One of the primary advantages is that electric machines offer faster response times. Since electricity can be delivered immediately, these machines can operate with high speeds and precision. This is particularly beneficial when manufacturing parts that require intricate detail or have tight tolerance specifications. Furthermore, electric machines typically have a longer lifespan due to fewer moving parts subject to wear and tear.
Maintenance requirements for electric injection molding machines are often less demanding because they lack hydraulic components that could leak or fail. This aspect contributes to a cleaner operating environment and lower ongoing maintenance costs. However, it should be noted that while electric injection molding machines are generally more expensive upfront than hydraulic ones, the cost can often be offset by the long-term savings in energy consumption and maintenance expenses.
|
Feature |
Description |
|
Power Source |
Electricity |
|
Energy Efficiency |
High due to precise control over motors and lack of hydraulics |
|
Precision & Repeatability |
Exceptionally high; beneficial for intricate parts with tight tolerances |
|
Speed |
Fast response times allowing quicker operational cycles |
|
Cleanliness |
Operates without hydraulic oil |
|
Maintenance |
Lower maintenance requirements; fewer wear-prone components |
|
Cost |
Higher initial investment but potential savings in long-term operation |

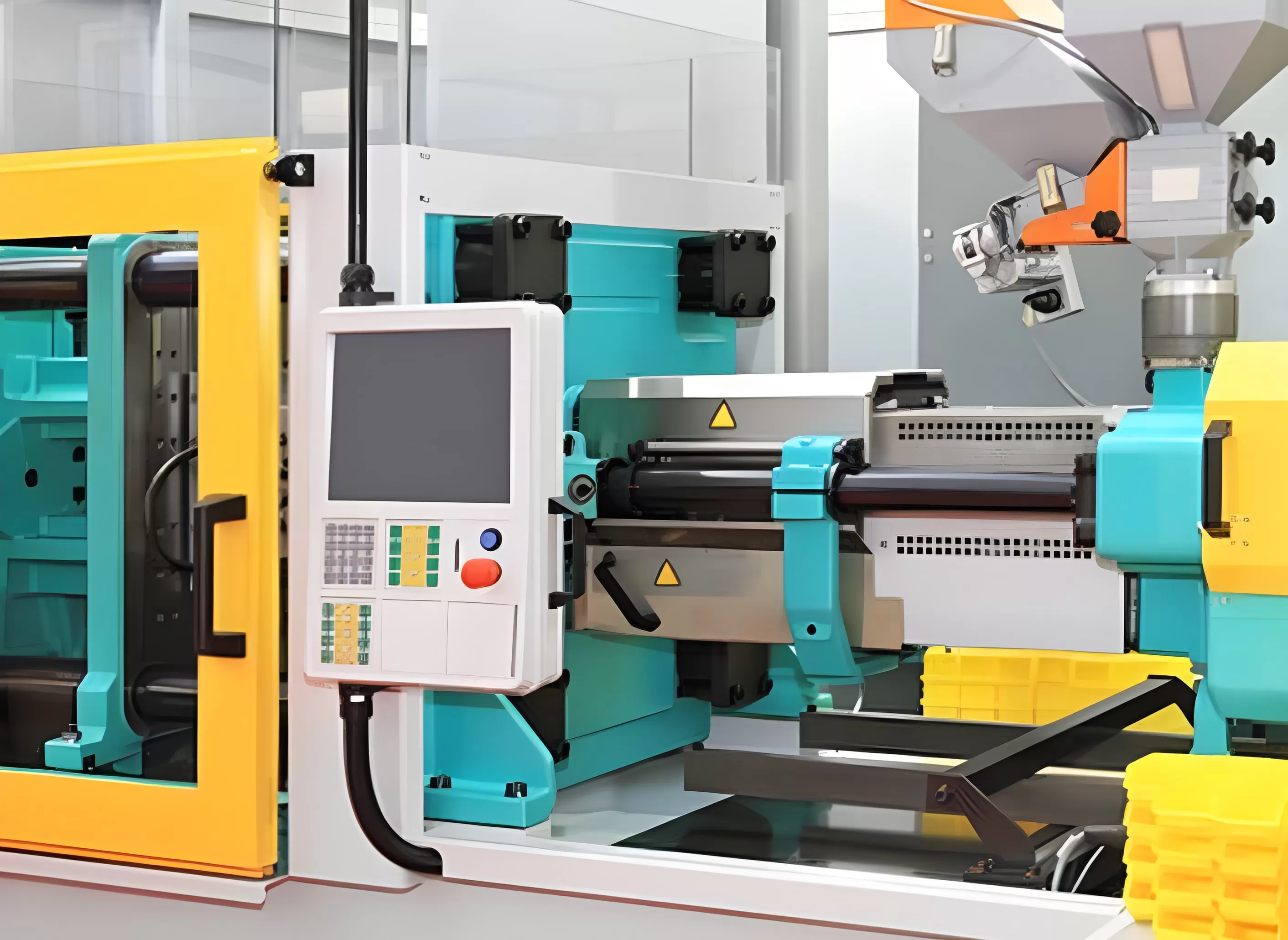
3.Hybrid Injection Molding Machine
Hybrid injection molding machines are a synergistic amalgam of the benefits offered by both electric and hydraulic molding systems. These advanced machines employ a combination of electrically driven mechanisms for precise control during processes like injection, metering, and mold opening/closing, while utilizing hydraulic actuators to facilitate actions requiring high force output such as clamping and ejection.
A key advantage of hybrid injection molding machines lies in energy efficiency. While they leverage the on-demand power characteristic of hydraulics for intense pressure application, they concurrently exploit the energy-saving capabilities inherent in electric systems for lower power tasks. This thoughtful integration results in lower operational costs compared to conventional hydraulic machines.
Precision is another salient feature attributed to hybrid models; with their electrical components ensuring meticulous control over processing parameters, product consistency and repeatability see significant enhancement. Furthermore, these machines offer faster cycle times due to their ability to simultaneously execute movements, thanks to separate drive systems.
Maintenance requirements for hybrids strike a balance between their counterparts; they’re less intensive than those demanded by wholly hydraulic models but slightly more so than purely electric variants. Capital cost consideration also places hybrid systems at an intermediate point – typically more economical than full-electric machines yet costlier than standard hydraulic ones.
|
Feature |
Advantage |
|
Combination of Electric & Hydraulic Systems |
Energy efficiency & precise control |
|
On-Demand Hydraulic Power |
High force output for clamping and ejection |
|
Electrical Drive Mechanisms |
Control & consistency in injection/metering |
|
Enhanced Precision |
Repeatable product quality |
|
Faster Cycle Times |
Simultaneous execution capabilities |
|
Balanced Maintenance |
Less demanding than full-hydraulic systems |
|
Cost |
Mid-range investment compared to other types |

Components of Injection Molding Machine
The two primary components of an injection molding machine are the injection unit and clamping unit.
|
Component |
Role |
Sub-components/Features |
|
Injection Unit |
Heats and injects molten material into mold |
Hopper, Screw, Barrel, Heater Bands |
|
Clamping Unit |
Holds mold in place for injection and cools down molds |
Mold Halves, Movable Platen, Toggle Mechanism |
1.Injection Unit
The injection unit of a plastic injection molding machine is the section where the plastic material is heated and injected into the mold cavity. This crucial component of the machine consists of several parts including the hopper, barrel, heater bands, screw, and nozzle. Plastic granules are fed into the hopper and then move towards the barrel where they get melted under high temperatures provided by surrounding heater bands.
The molten plastic is then conveyed towards the mold by the rotation of a screw which also acts as a plunger during injection. The torque and speed of this screw are adjustable to provide precise control over the volume and rate at which molten plastic is injected. Before injection begins, a nozzle attached to the end of the barrel presses against the mold to create a tight seal, ensuring that no material leaks during injection.
Once sufficient material has filled up in front of the screw, it rapidly thrusts forward within the barrel, forcing melted plastic through the nozzle and into the mold cavities where it will cool down and solidify forming finished parts after being opened by clamping unit. Consistency in temperature control throughout this process is essential as it influences both part quality and cycle time. Advanced machines often employ computer-aided controls for better precision in various stages such as melting pressure, temperature settings, shot size, and screw velocity.
|
Component |
Function |
|
Hopper |
Holds and feeds plastic granules into barrel |
|
Barrel |
Heats up granules turning them into melt |
|
Heater Bands |
Provide heat needed for melting plastic |
|
Screw |
Rotates to mix/advance material; acts as plunger during injection |
|
Nozzle |
Delivers molten plastic from barrel into mold |
|
Temperature Control System |
Maintains consistent melt temperature |
|
Shot Size Adjustability |
Allows control over amount of plastic injected |
|
Screw Velocity |
Controllable speed for screw rotation/injection |
2.Clamping Unit
The clamping unit primary function is to open and close the mold and facilitate ejection of the molded parts. During operation, after the polymer has been injected into a mold cavity, the clamping unit holds the mold halves tightly together under pressure to counteract the force of injection. This ensures accurate shot weights and consistent molding quality by preventing leakage of molten plastic.
Clamping systems are typically classified by their method of actuation and controlled via hydraulic, mechanical, or electrical means. The clamping force that these units can exert is an essential parameter when selecting an injection molding machine for specific applications since it dictates what size and types of products can be produced.
The design incorporates components such as a movable platen, stationary platen, tie bars, toggle mechanism for some machines particularly those employing mechanical or hydraulic operation, and an ejection system that helps remove finished parts from within the mold once it opens.
In summary, the clamping unit's efficiency influences cycle times and precision in manufactured parts which directly affects production throughput and quality measures in any plastic injection molding process.
|
Component |
Function |
|
Movable Platen |
Holds one half of the mold and moves to open/close it |
|
Stationary Platen |
Secures the other half of the mold |
|
Tie Bars |
Guide movement and maintain alignment between platens |
|
Toggle Mechanism (if present) |
Facilitates opening/closing with mechanical advantage |
|
Ejection System |
Pushes out finished product from opened mold |
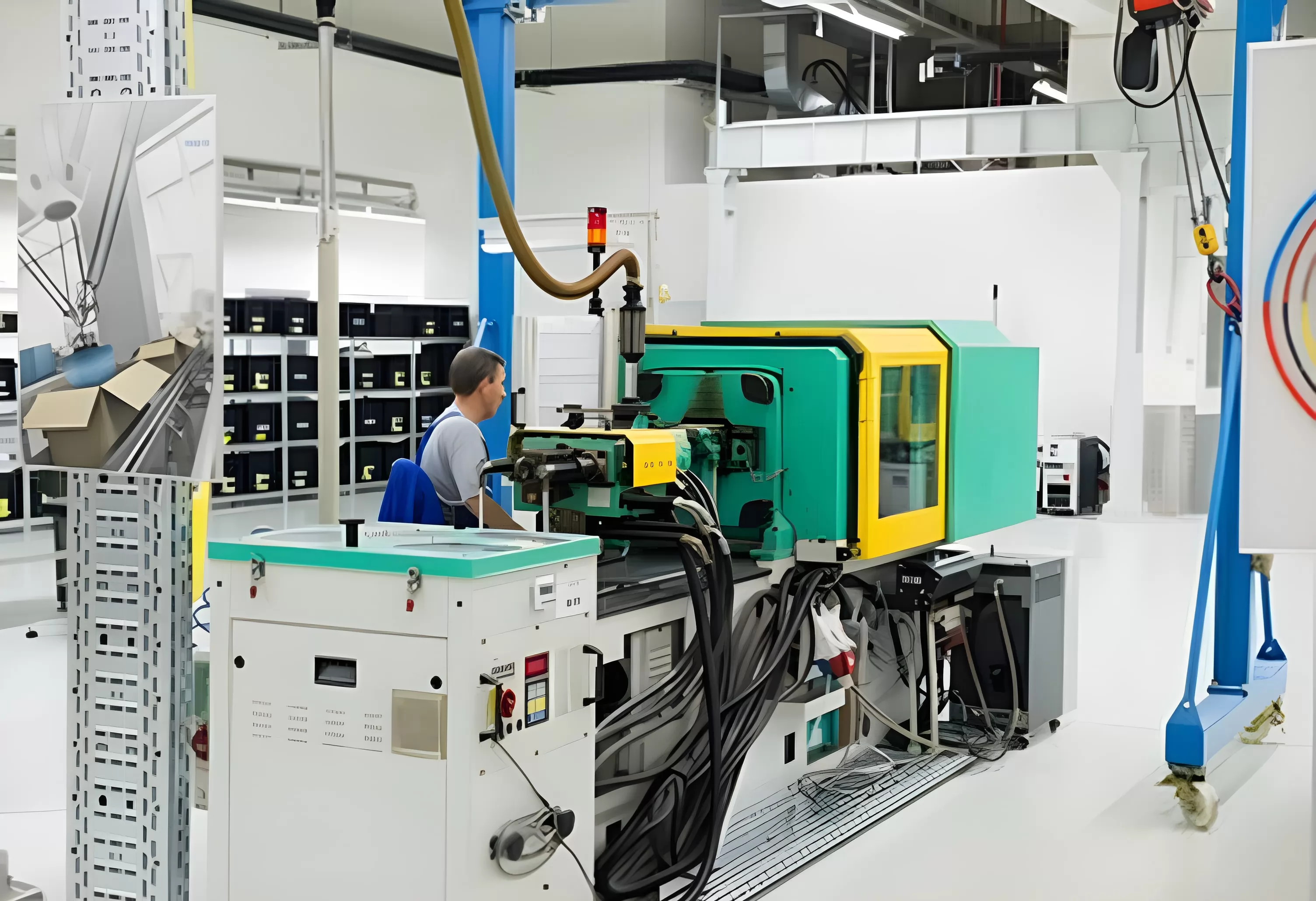
How Big Are Plastic Injection Molding Machines?
The size of plastic injection molding machines can vary dramatically, ranging from small benchtop units to large, industrial-scale machines. The footprint of these machines typically correlates with their clamping force and shot size, which are measures of their capability to fabricate larger or more complex parts.
Smaller plastic injection molding machines may have a clamping force as low as 5 tons and can easily fit within a small workshop or laboratory setting. These compact units are often used for the production of small components such as medical devices, consumer electronics parts, or intricate toys.
On the other end of the spectrum, larger plastic injection molding machines boast clamping forces that can exceed 6,000 tons and require extensive floor space; comparable to an industrial warehouse. Such large-scale machines are utilized for the manufacturing of substantial components like automotive parts, storage containers, and furniture.
The physical dimensions also depend on whether the machine is a vertical or horizontal press. Vertical injection molding machines tend to have smaller bases but can be taller than horizontal presses; this makes vertical presses suitable for factories with limited floor space but sufficient headroom.

How Much Does a Plastic Injection Molding Machine Cost?
The cost of plastic injection molding machines can vary significantly based on various factors including size, type, and the specific needs of an application. Generally, the pricing ranges from $25,000 for a simple small-scale machine to upwards of $200,000 for large, complex systems. Entry-level models typically used for prototyping or limited production runs are at the lower end of this spectrum.
For industrial-grade machines that offer higher precision and larger part production capabilities, prices increase accordingly. Hydraulic injection molding machines tend to be less expensive than their electric counterparts but are also less energy-efficient. Meanwhile, electric machines offer faster cycle times and greater energy efficiency but at a higher initial cost.
More technologically advanced options like hybrid injection molding machines, which combine attributes of both hydraulic and electric systems to balance cost-efficiency with performance optimization, can fluctuate in price based on configuration and capacity specs.
Additionally, customization options such as enhanced control systems or specialty software integration for automation could further impact the investment required. It is also important to consider ancillary costs such as shipping, installation, training, maintenance expenses when budgeting for a plastic injection molding machine.
Lastly, it is wise to factor in the resale value; high-quality brands may hold value better over time than lesser-known manufacturers.
In conclusion
In summary, a plastic injection molding machine is a highly efficient and versatile tool used to produce complex and precise plastic components at a high volume.
If you're seeking to enhance your manufacturing capabilities or wish to learn more about incorporating this technology into your production line, consider consulting with an industry expert today. Discover the potential of precision and efficiency that plastic injection molding machines can bring to your business operations.