EPDM injection molding is a specialized manufacturing process used to produce high-quality rubber components from EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber. This process involves injecting molten EPDM into a mold cavity under high pressure, where it cools and solidifies to form the desired part. EPDM is renowned for its exceptional resistance to heat, weathering, and chemicals, making it the material of choice for various industries, including automotive, construction, and consumer goods. By leveraging the precision and efficiency of injection molding, manufacturers can produce durable, complex rubber parts with a high degree of accuracy.
You will learn from article:
What Is EPDM Rubber?

Before diving into the EPDM injection molding process, it's essential to understand what makes EPDM rubber unique. EPDM is a type of synthetic rubber known for its impressive durability and resilience. It consists of ethylene and propylene monomers, cross-linked with diene to create its distinct molecular structure. This structure provides EPDM with outstanding resistance to environmental elements such as UV rays, ozone, and extreme temperatures, which is why it's commonly used in demanding applications like weather stripping, seals, hoses, and roofing membranes.
Learn more: (EPDM Rubber Wikipedia.)
Pros of EPDM Rubber
-
Exceptional durability: EPDM rubber is highly durable and resistant to environmental conditions, ensuring long-term performance in various applications.
-
Weather resistance: It exhibits remarkable resistance to weathering, UV radiation, ozone, and aging, making it ideal for outdoor use.
-
Water resistance: EPDM offers excellent sealing capabilities, preventing water ingress and protecting structures from water damage, particularly in roofing and window applications.
-
Flexibility: Its superior flexibility remains intact even under frequent temperature fluctuations, ensuring longevity and reliability.
-
Chemical resistance: EPDM is resistant to acids, alkalis, and other chemicals, making it suitable for industrial environments where chemical exposure is common.
-
Recyclability: At the end of its service life, EPDM can be recycled or repurposed, contributing to sustainability efforts and reducing waste.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Its longevity and minimal maintenance requirements make it a cost-effective solution over time in various industries.
-
Versatility: EPDM rubber finds applications in automotive manufacturing, construction, and other fields due to its wide-ranging benefits and adaptability.
Cons of EPDM Rubber
-
Susceptibility to damage from petroleum-based products and certain types of oils: EPDM rubber can be easily damaged by exposure to petroleum-based products and certain oils, limiting its usability in environments where such substances are prevalent.
-
Temperature sensitivity: EPDM rubber may experience degradation when subjected to extreme heat over prolonged periods, necessitating careful consideration in high-temperature applications or environments.
-
Intricate installation process: Installing EPDM roofing materials can be complex and requires skilled labor to ensure proper sealing and fitting. Incorrect installation may lead to leaks and reduced lifespan of the material, highlighting the importance of expertise during installation.
-
Limited resistance to abrasion and tearing: While durable, EPDM rubber does not offer the same level of resistance to abrasion and tearing as some other materials. This limitation may reduce its effectiveness in scenarios where mechanical wear is a significant factor.
What Is EPDM Injection Molding?
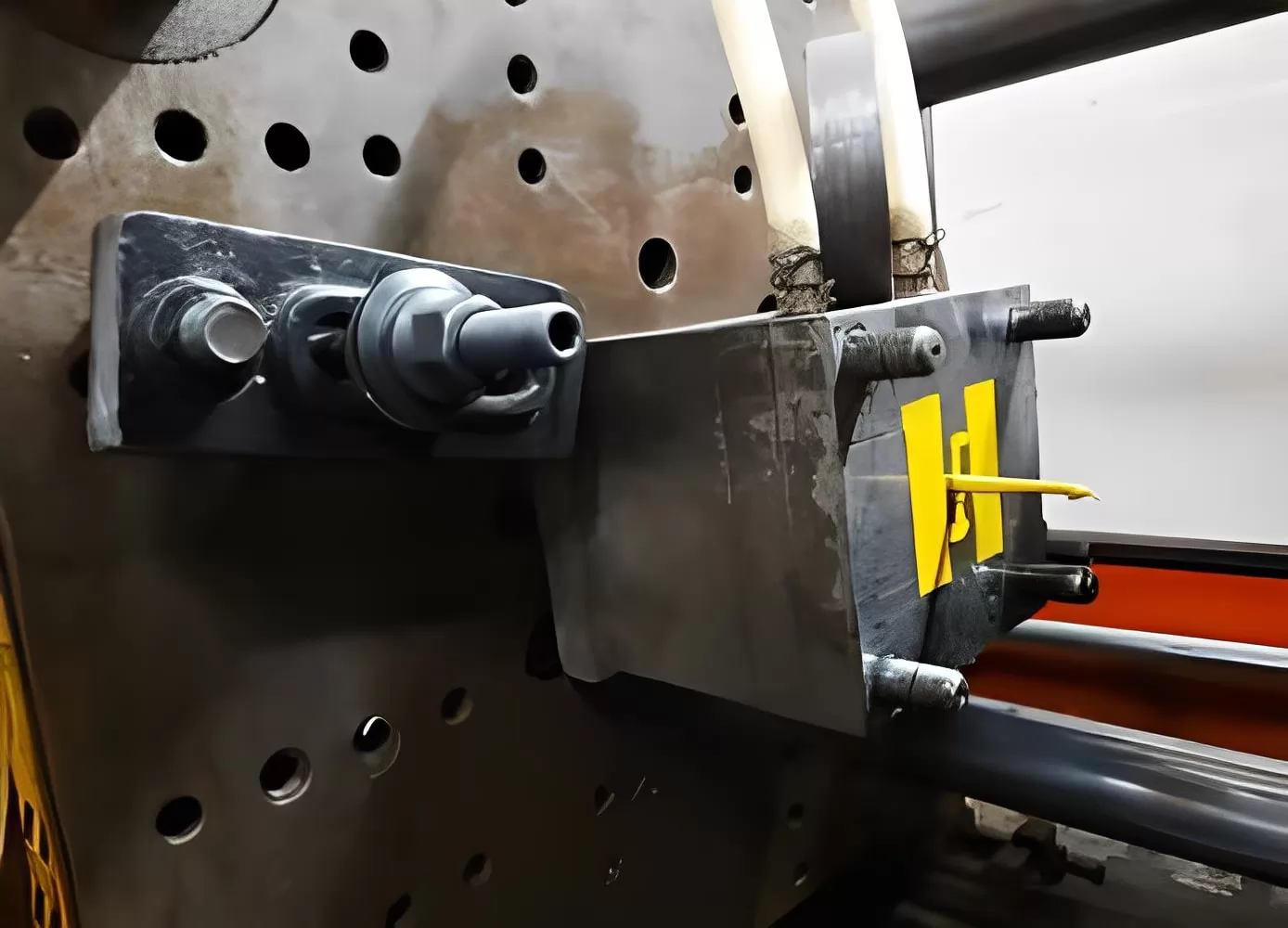
EPDM injection molding is a specialized manufacturing process used to shape EPDM rubber—a synthetic material known for its outstanding heat, ozone, and weather resistance—into a variety of complex forms and precision parts. This method involves injecting molten EPDM rubber into a mold cavity under high pressure. Once the material cools down and solidifies, the newly formed part can be ejected out of the mold, ready for use or further processing.
The technique stands out because it allows for mass production of consistent, high-quality rubber components with intricate shapes and fine details that might be difficult or impossible to achieve through other molding methods. The use of EPDM, specifically in this process, offers products that benefit from the robust properties of this type of synthetic rubber, including excellent UV stability, thermal resistance, and flexibility across a wide range of temperatures.
Injection molding with EPDM opens up possibilities for creating durable components that see widespread use across various industries such as automotive (for door seals, hoses), construction (window seals), and consumer goods among many others. This efficiency-driven process ensures lower waste production compared to traditional methods, making it an environmentally conscious choice for manufacturers looking to minimize their carbon footprint while optimizing resource-use efficiency.
By leveraging precise control over every stage—from raw material heating to rapid cooling in the mold—manufacturers can produce parts that require minimal finishing work, saving both time and resources. As such, EPDM injection molding has become a preferred method for producing components that combine complex geometrical features with the exceptional durability and performance characteristics inherent to EPDM rubber.
Can You Injection Mold EPDM?
Yes, you can injection mold EPDM rubber, and this is one of the most effective methods for producing complex, high-performance rubber parts. The EPDM injection molding process allows for the creation of intricate geometries with tight tolerances, which would be challenging or even impossible to achieve using other manufacturing methods. Thanks to its thermoset properties, EPDM retains its shape and structure after molding, making it ideal for components that must withstand harsh conditions.
Advancements in technology have improved the efficiency of EPDM injection molding, making it more cost-effective and versatile. With the ability to produce high-quality parts quickly and with minimal waste, EPDM injection molding has become a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
Advantages of EPDM Injection Molding

EPDM injection molding offers several key benefits, which contribute to its widespread use across various industries:
-
High Material Compatibility: EPDM’s resistance to heat, UV light, ozone, and chemicals makes it ideal for demanding applications.
-
Efficiency: Injection molding ensures fast cycle times, reducing production costs and meeting high-volume demands.
-
Precision: The process allows for the production of complex shapes and tight tolerances with high consistency.
-
Durability: EPDM parts retain their physical properties over time, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
-
Flexibility: EPDM injection molding offers design flexibility, allowing for easy adjustments to molds and part designs without significant delays or cost increases.
What Is the EPDM Injection Molding Process
The EPDM injection molding process involves several key steps that ensure the material is shaped precisely to meet specific requirements. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Step 1: Material Preparation
The raw EPDM rubber material, typically in pellet form, is prepared for injection molding.
Step 2: Loading
The prepared EPDM pellets are loaded into the hopper of the injection molding machine.
Step 3: Heating and Melting
The pellets are then fed into the machine’s heating chamber, where they are melted to a molten state. This step requires precise temperature control to maintain the chemical integrity of the EPDM material.
Step 4: Injection
Once the material is molten, it is injected into the mold cavity at high pressure. This ensures the mold is filled accurately without compromising product quality.
Step 5: Cooling and Solidification
The mold holds the molten EPDM under pressure as it cools and solidifies. This step is crucial, as uniform cooling helps prevent defects like warping or poor feature definition.
Step 6: Ejection
After the material has solidified, the mold opens, and the newly formed EPDM component is ejected from the mold.
Step 7: Post-Processing
In some cases, post-processing steps such as trimming or additional curing may be required to ensure the part meets all necessary specifications.
Why Choose EPDM Injection Molding?
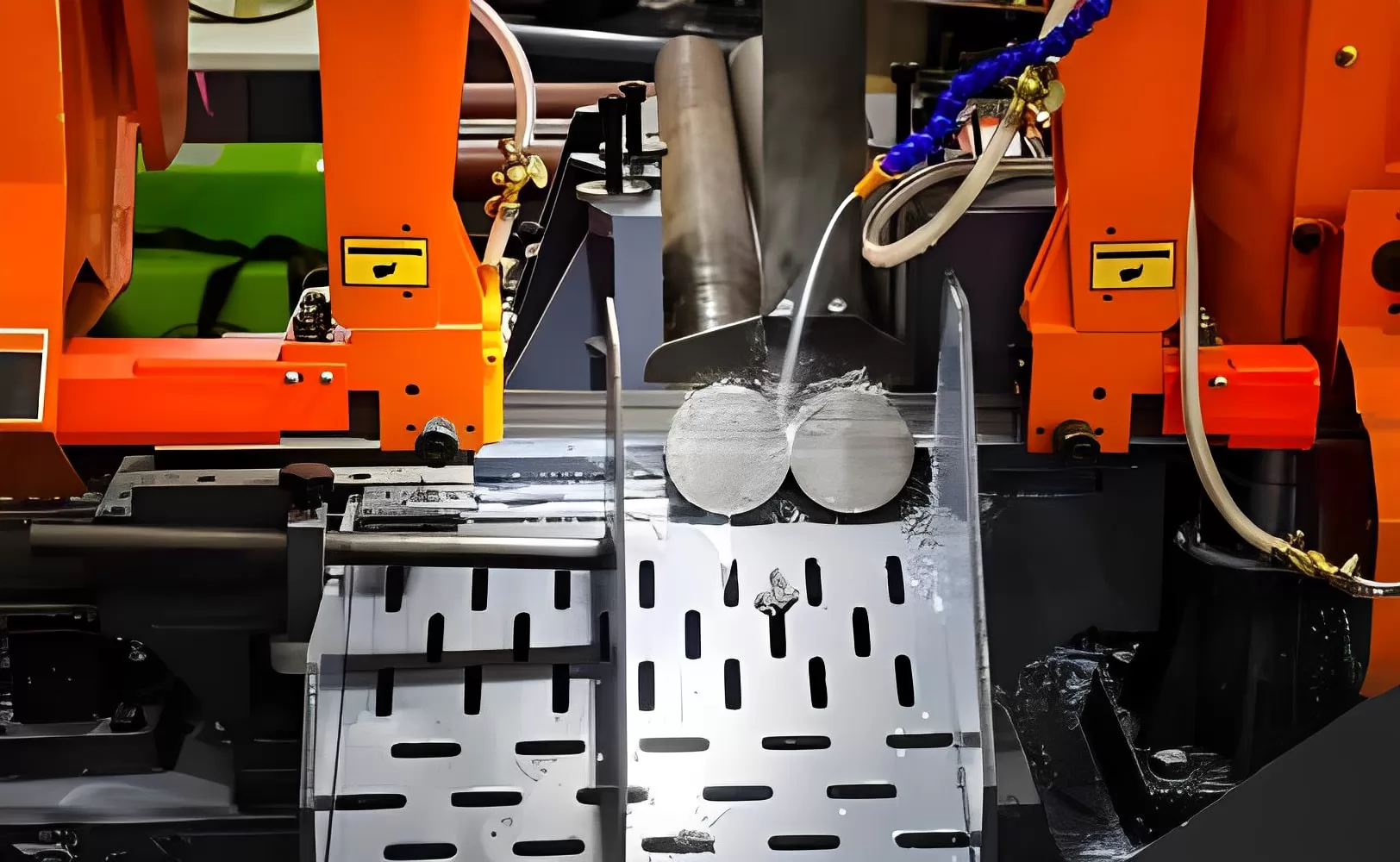
The question isn’t whether you can injection mold EPDM—you absolutely can. The real question is why this process is so beneficial for manufacturing high-performance rubber parts. Here are a few reasons why EPDM injection molding is a popular choice:
-
Efficiency in Production: EPDM injection molding enables quick cycle times, reducing production costs and allowing manufacturers to meet high-volume demands without compromising on quality.
-
High Precision: With EPDM injection molding, you can produce parts with intricate geometries and tight tolerances, making it ideal for applications in automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
-
Durability and Long-Term Stability: Parts made from EPDM rubber retain their excellent resistance to weathering, chemicals, and heat, ensuring long-term performance even under challenging conditions.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: The injection molding process for EPDM minimizes material waste and reduces labor costs, making it an affordable solution for large-scale production.
-
Flexibility: The process allows for design modifications and adjustments, enabling manufacturers to respond quickly to changes in customer requirements or product specifications.
What EPDM Parts Can Be Injection Molded?
-
Automotive industries: EPDM is commonly used for producing parts like window seals, door seals, hoses, belts, and gaskets due to its excellent resistance to environmental factors such as UV rays and ozone.
-
Construction sector: EPDM finds applications in roofing membranes and electrical gaskets due to its impermeability to water and resistance to temperature variations, making it ideal for outdoor constructions exposed to diverse climatic conditions.
-
Consumer goods: EPDM injection molding is utilized for manufacturing waterproof footwear, garden hoses, and appliance parts, taking advantage of its versatile characteristics including heat resistance, flexibility over a wide temperature range, and overall durability.
-
Industrial applications: EPDM is employed in producing o-rings, mechanical seals, and vibration damping components due to its chemical inertness, making it suitable for use in environments involving mild acids, detergents, alkalis, silicone oils, and greases.
Conclusion
EPDM injection molding is a highly efficient, cost-effective, and precise manufacturing process that is widely used across various industries to produce durable rubber components. By understanding the EPDM injection molding process and the unique advantages it offers, manufacturers can leverage this method to create high-performance parts that meet the demands of tough applications. Whether you are producing automotive parts, roofing seals, or industrial components, EPDM injection molding offers a reliable and versatile solution for your manufacturing needs.
If you’re considering EPDM injection molding for your next project, don’t hesitate to explore how this process can enhance your product's performance and durability. Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist with your EPDM molding requirements.